Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
Differentiable volume Rendering will require a lot of storage. This is undesirable if we want to transmit this information over the network.
NeRF is one of the first techniques to model a 3D scene that requires less disk space and also captures the fine geometry and texture of complex scenes.
Challenge of View Synthesis
The challenge is to synthesize new views of a 3D scene using a small number of available 2D snapshots of the scene. The challenge is to construct complete information about the world given incomplete and noisy information.
## Radiance Fields Radiance is the intensity of a point in space when viewed in a particular direction. When capturing this information in RGB, the radiance will have three components corresponding to the colors Red, Green, and Blue. The radiance of a point in space can depend on many factors, including the following:
- Light sources illuminating that point
- The existence of a surface (or volume density) that can reflect light at that point
- The texture properties of the surface
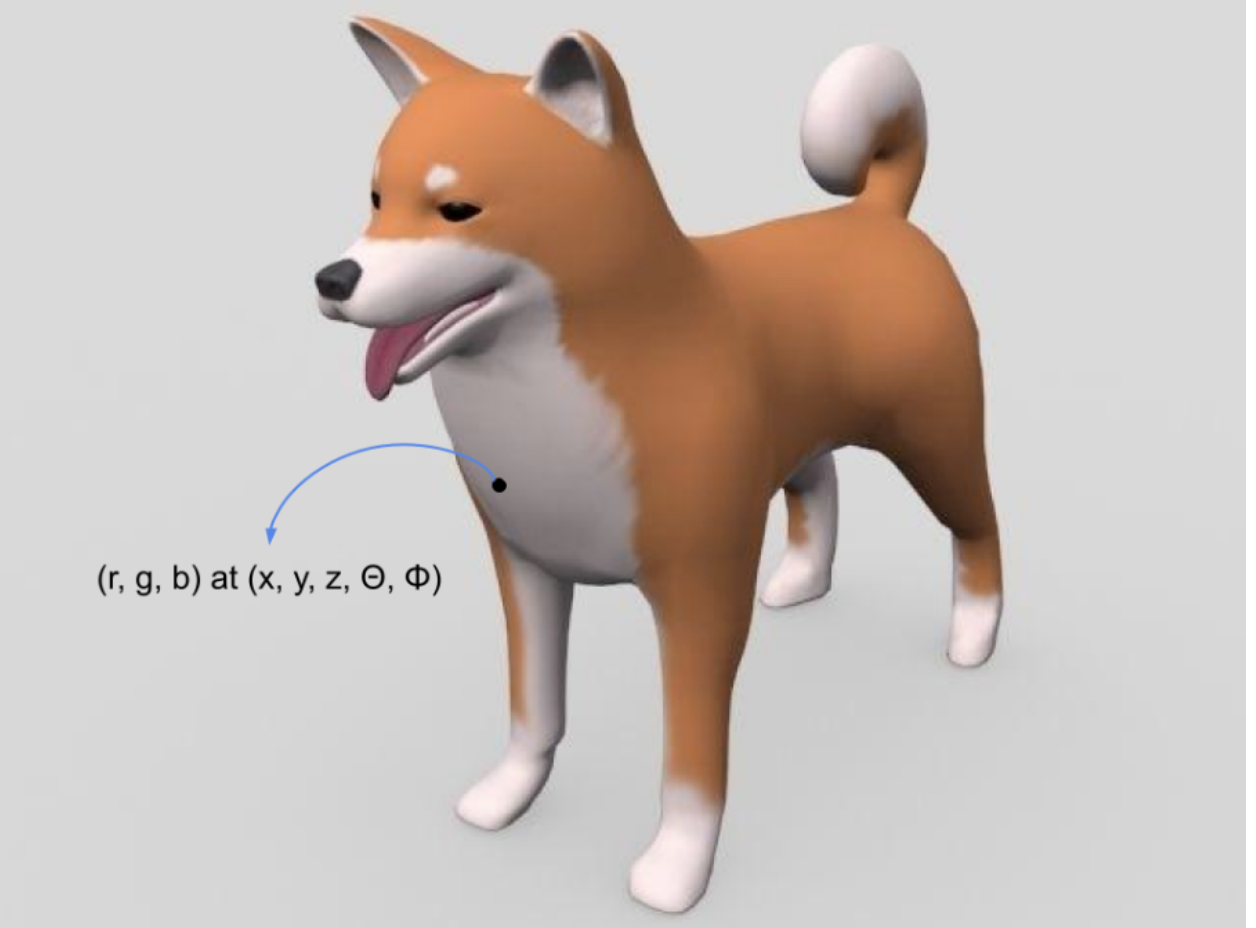

If we know the radiance of all the points in a scene in all directions then it constitutes a radiance field.
Radiance fields with Neural Networks
NeRF uses a neural network to represent a volumetric scene function. This neural network takes a 5-dimensional input. These are the three spatial locations (x, y, z) and two viewing angles (θ, ∅). Its output is the volume density σ at (x, y, z) and the emitted color (r, g, b) of the point (x, y, z) when viewed from the viewing angle (θ, ∅).
The model therefore maps any point in the 3D scene and a viewing angle to the volume density and radiance at that point. You can then use this model to synthesize views by querying the 5D coordinates along camera rays and using the volume rendering technique to project the output colors and volume densities into an image.
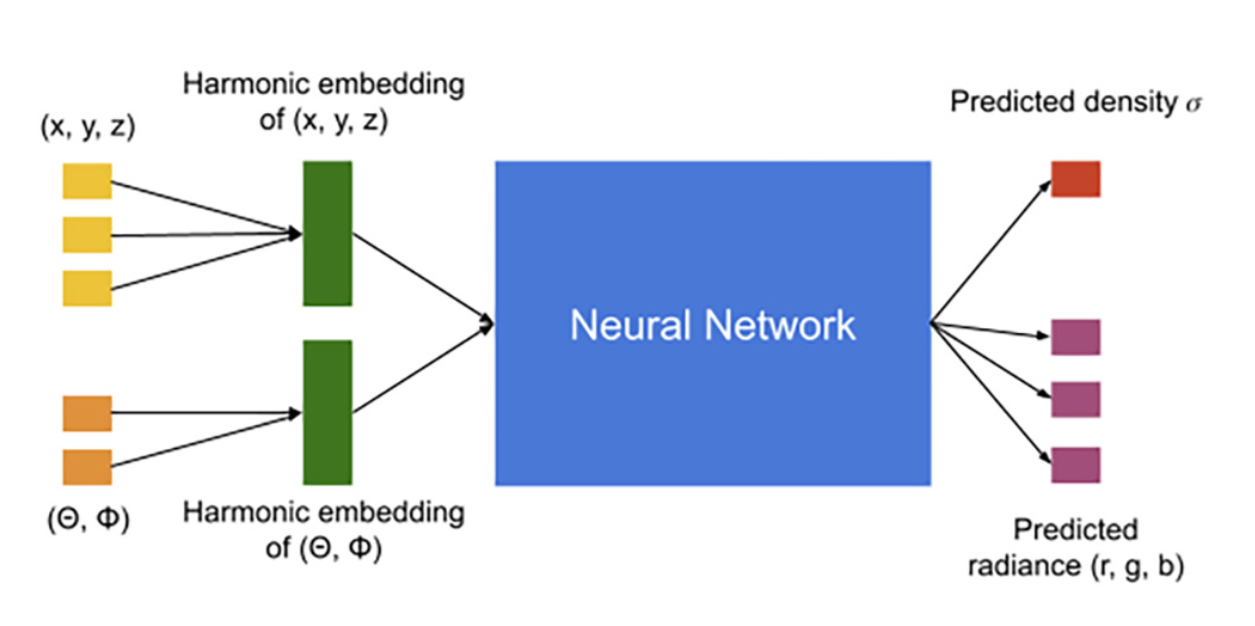
A single NeRF model is optimized on a set of images from a single scene. Therefore, each model only knows the scene on which it is optimized. NeRF is optimized to generalize unseen viewpoints well for a particular scene.