Latent Dirichlet Allocation
Blueprint for the LDA Machine
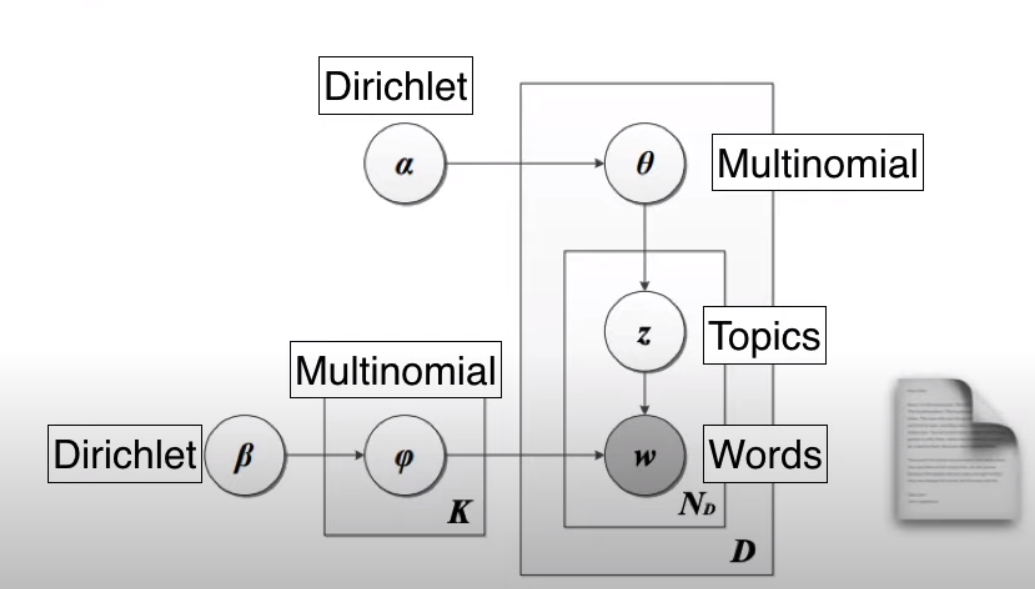
LDA Blueprint 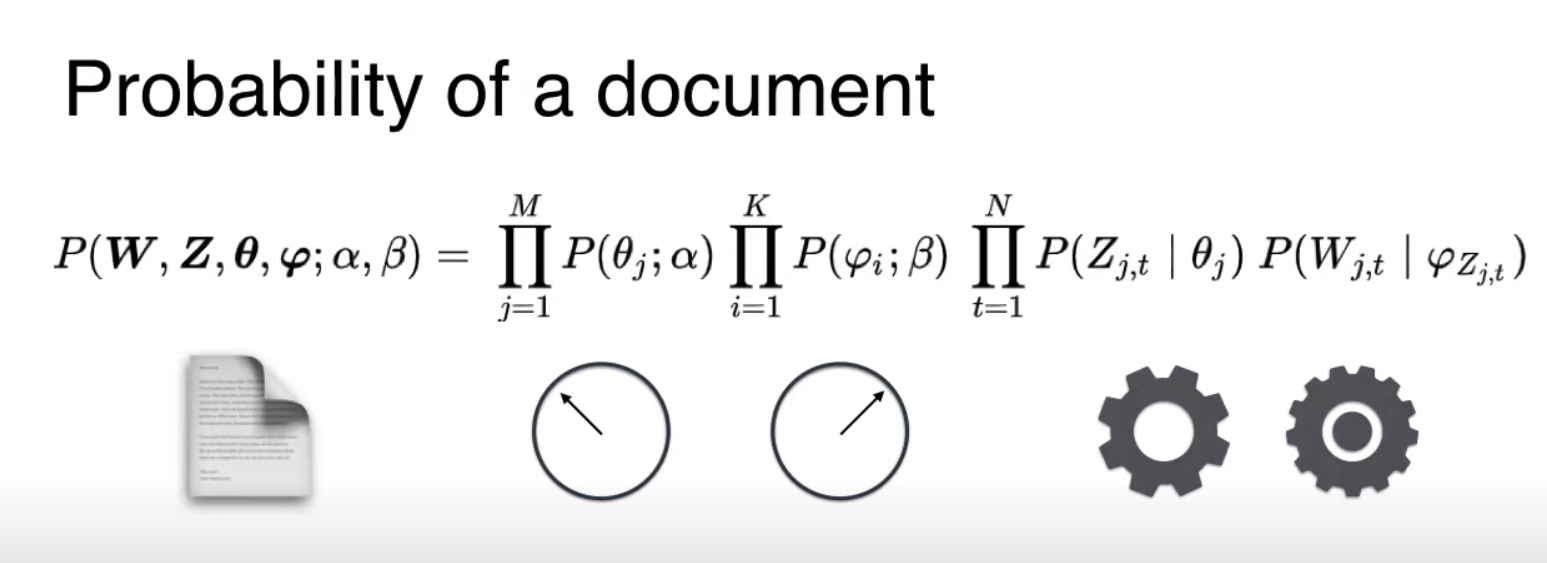
Probability of a document 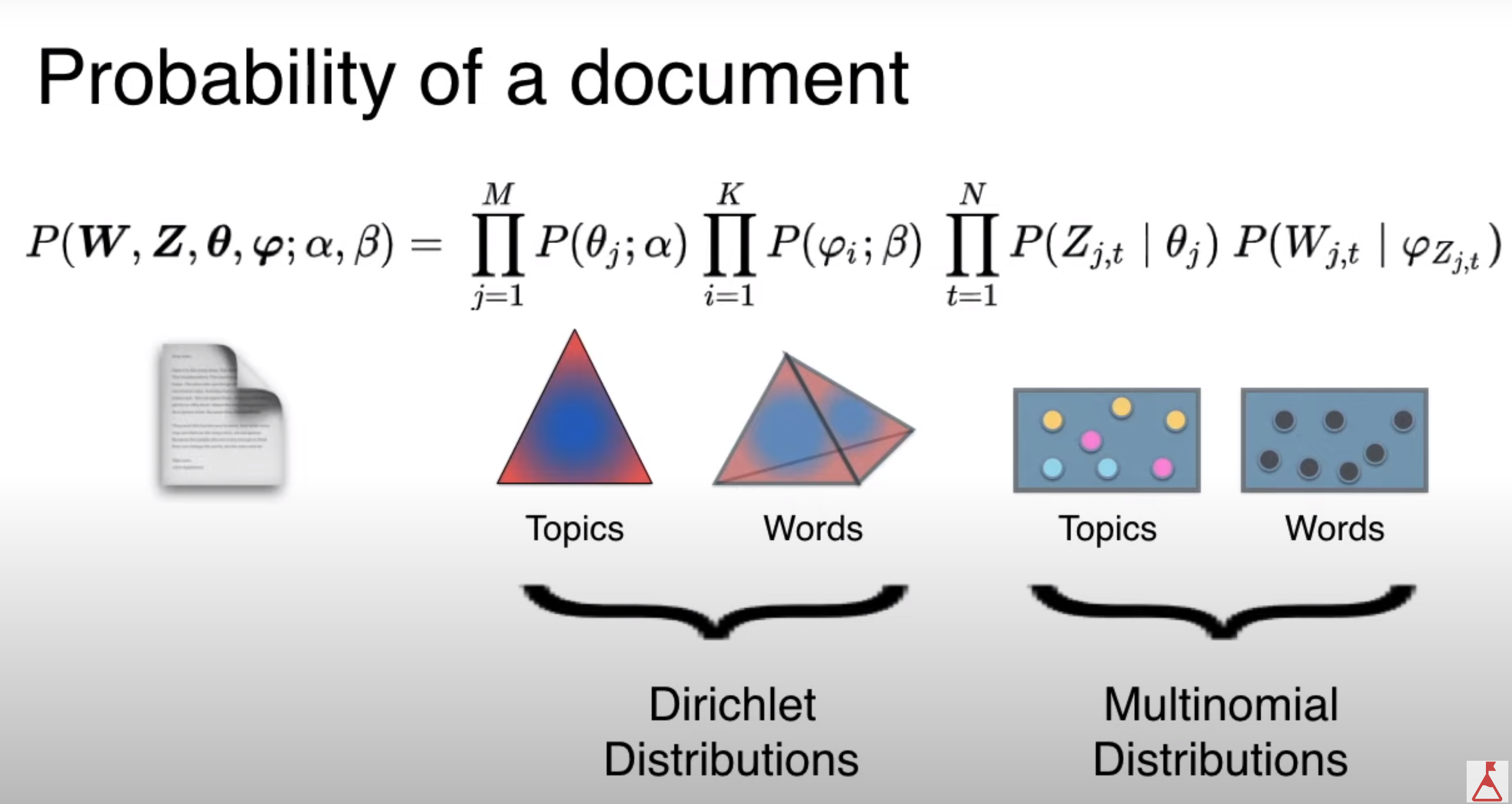
Probability of a document 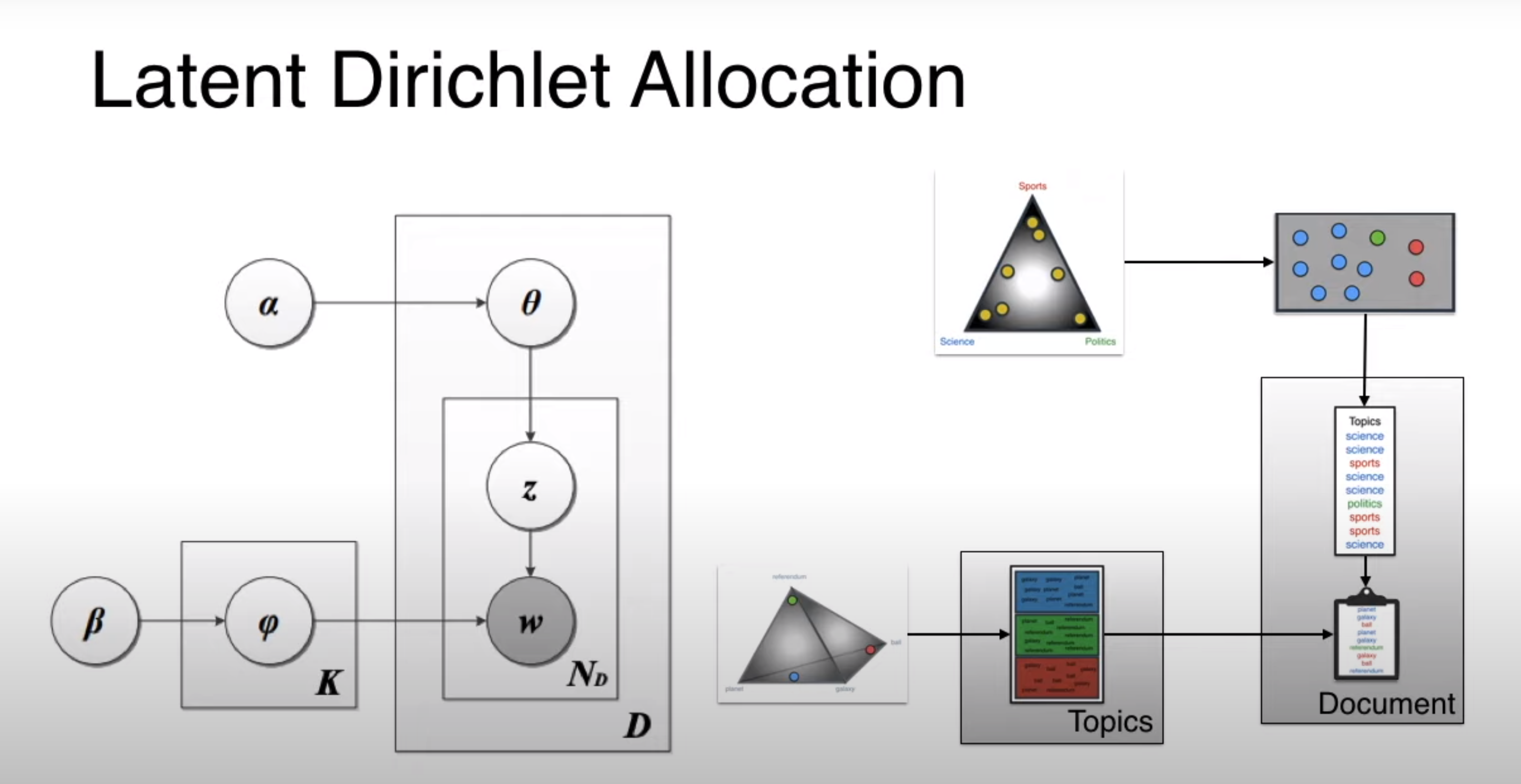
LDA Blueprint with what they are doing
Dirichlet Allocation
In this distribution we have a parameter `alpha’. Depending on the values of alpha we will get different distributions.
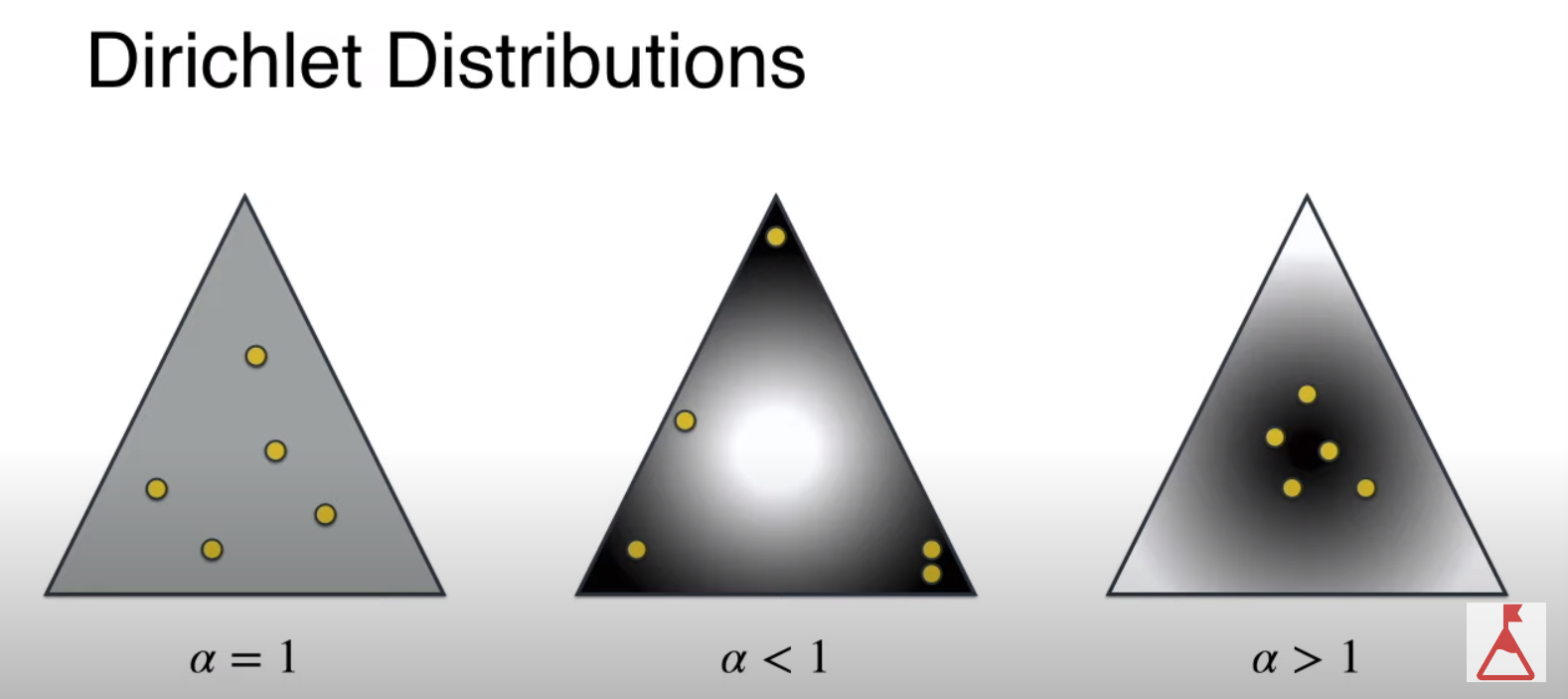
Dirichlet distributions based on alpha values we consider two Dirichlet distributions - One which will associate document with topics and the other topics with words
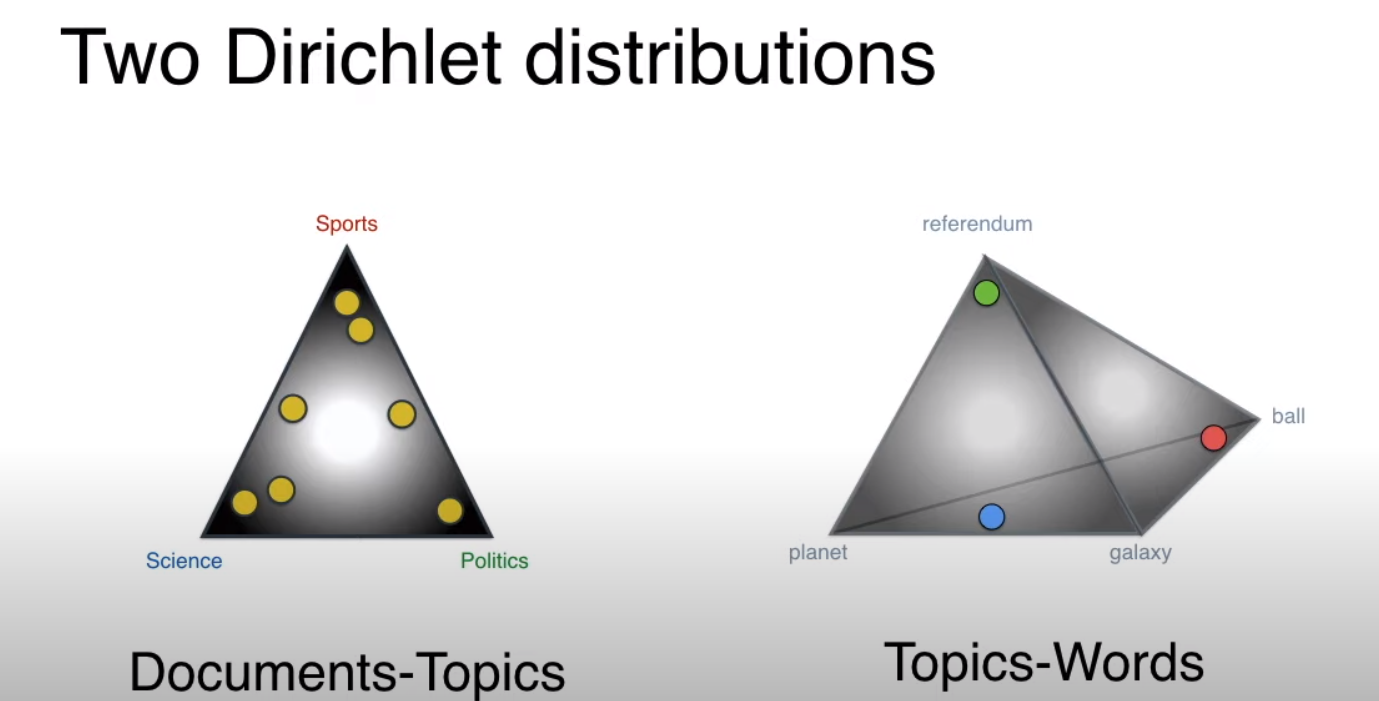
Two Dirichlet distributions These two Dirichlet distributions are the parameters in the blueprint. We generate different documents by adjusting the points in these two distributions
Two Dirichlet distributions as knobs in the blueprint
How LDA works
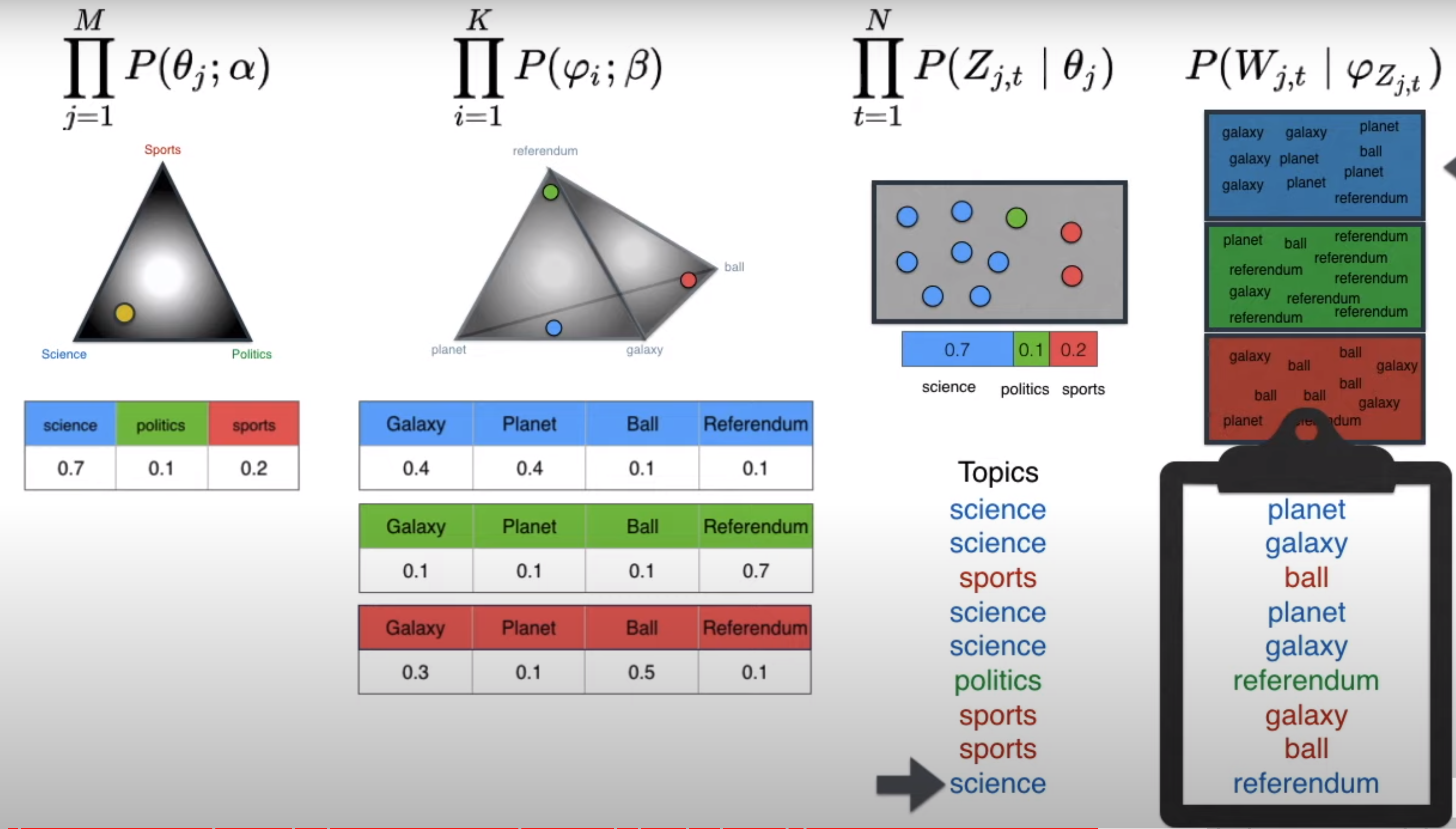
LDA in action We generate documents by assigning documents to topics and topics to words. The probability of generating the same article as training data will be very low.
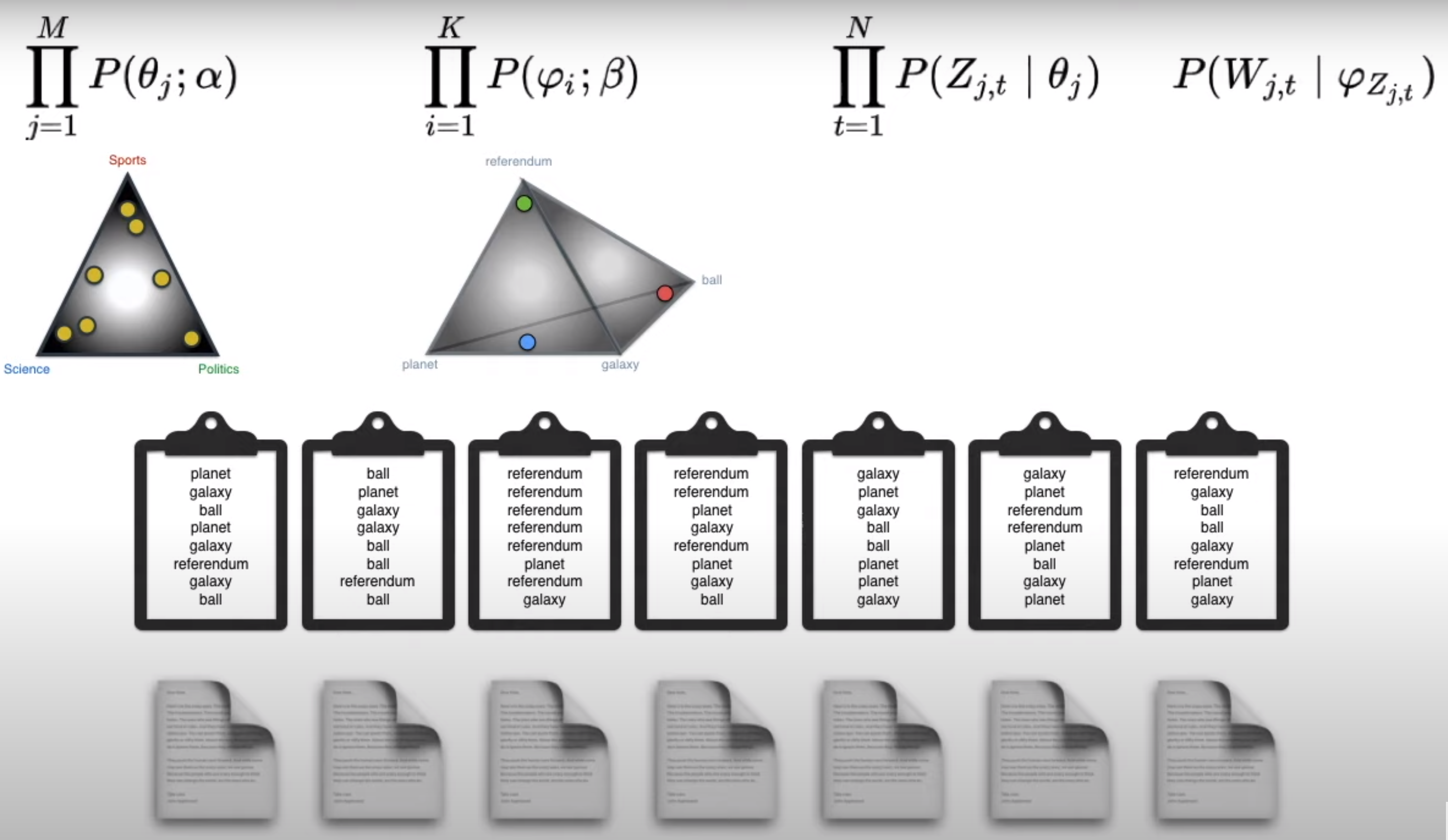
Generating documents with assigning of topics for different documents and assigning topics to different words 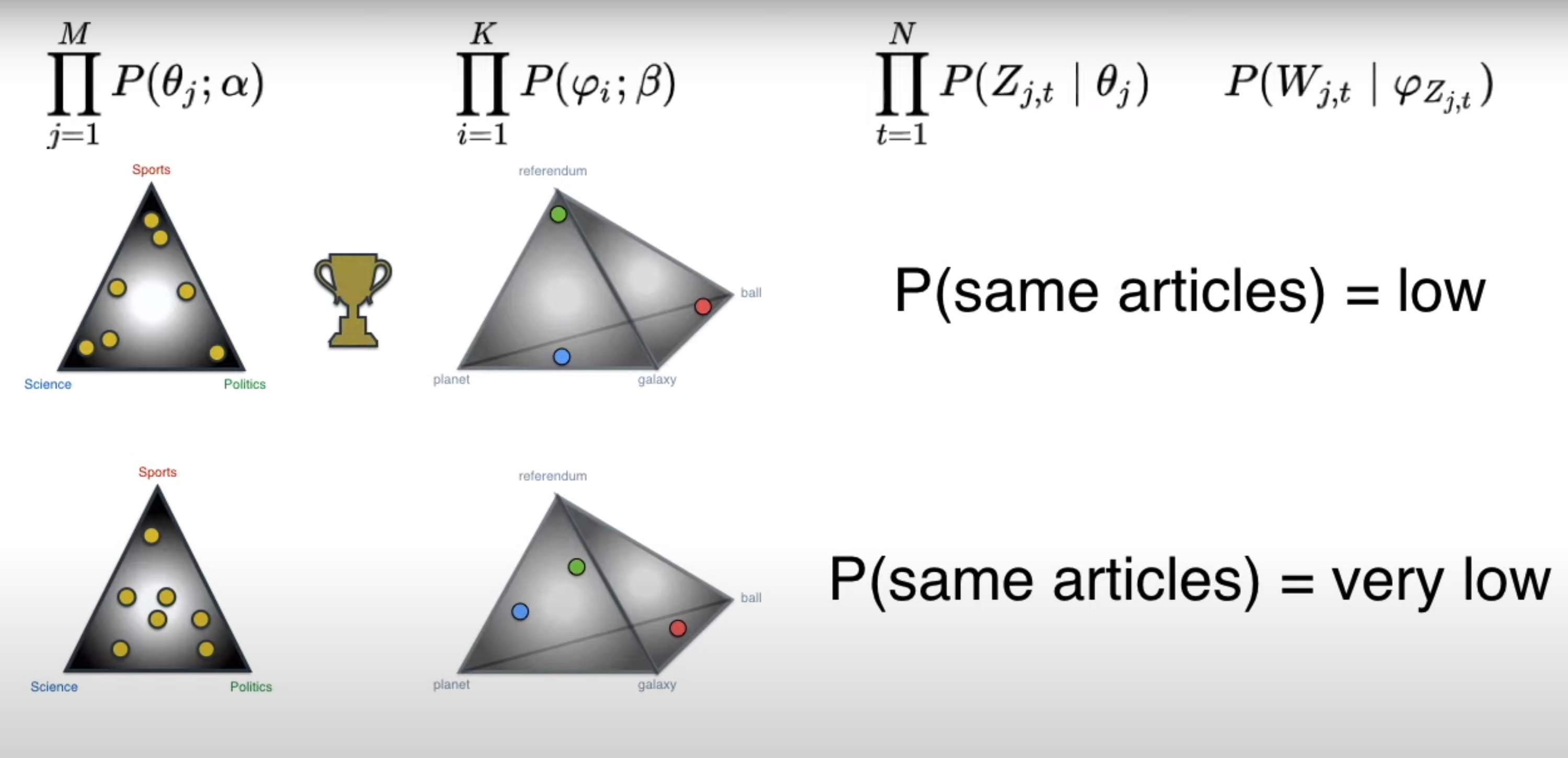
Comparing the probability of the document generated with the ground-truth
Training LDA
- The number of topcis is a hyperparameter
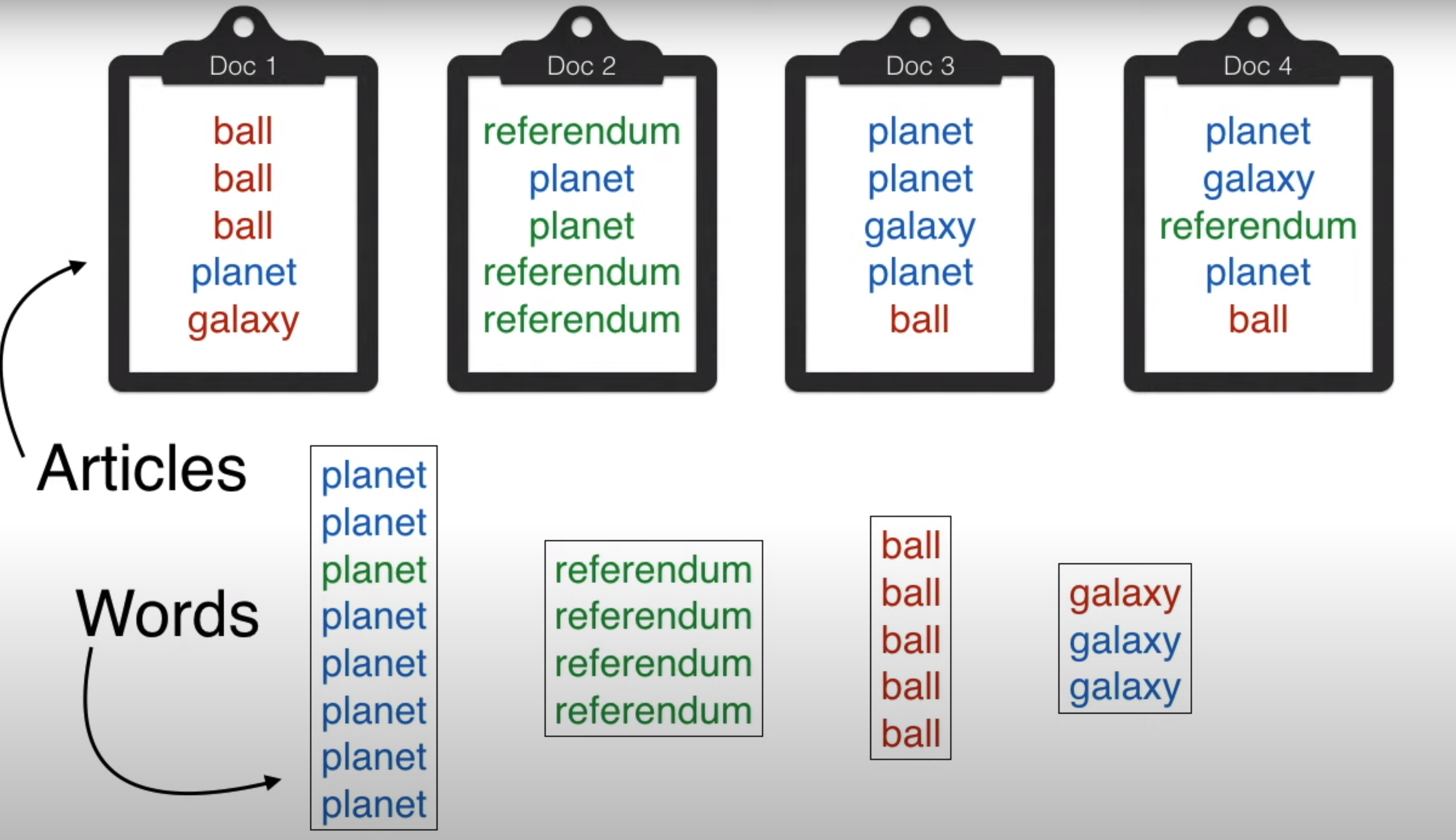
Gibbs Sampling
Gibbs Sampling in the context of LDA is trying to tag the words in the document to be monochromatic (belonging to a single category) and trying to tag the document to be monochromatic

Gibbs Sampling 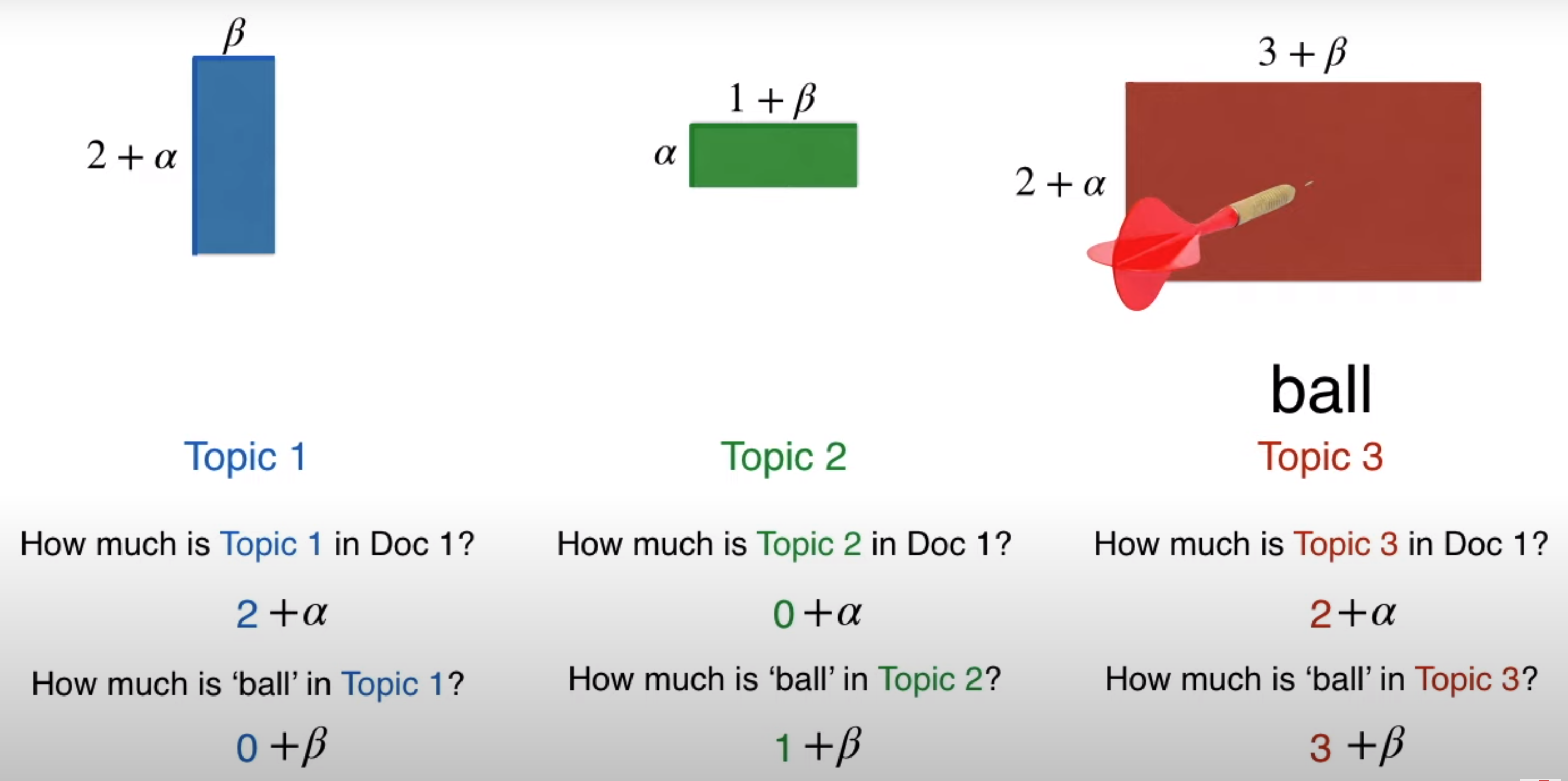
Ensuring we are considering all the topics are considered in Gibbs sampling 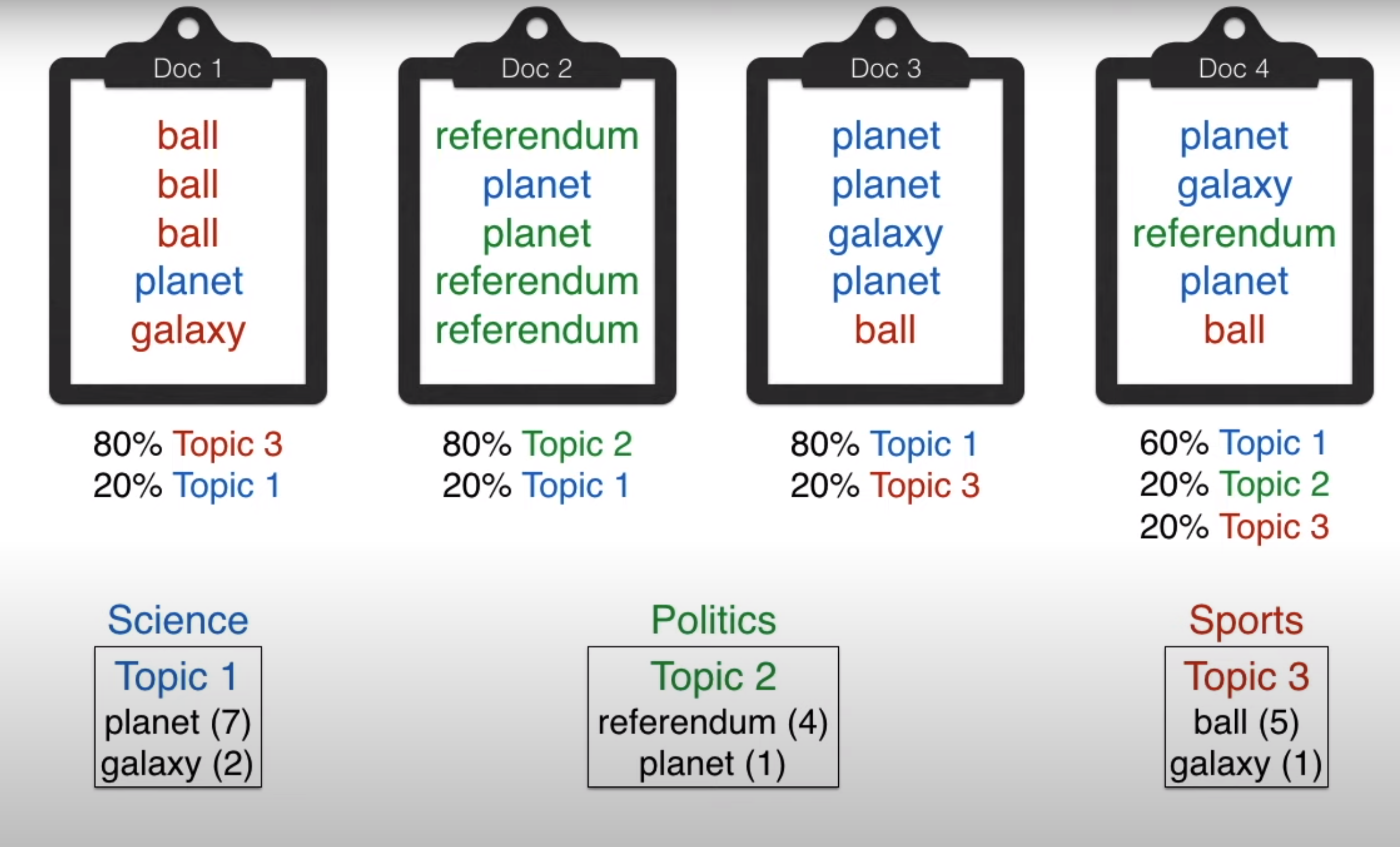
Assigning to topics to documents based on assigning topics to words Maximizing the probability of the LDA equation is very difficult. Hence we use Gibbs sampling
Gibbs sampling explained by chatgpt
Gibbs sampling is a statistical algorithm used to generate samples from a probability distribution that might be too complex to calculate directly. It is often used in Bayesian inference, where the goal is to estimate the unknown parameters of a model given some observed data.
The idea behind Gibbs sampling is to iteratively sample from the conditional distributions of each variable in the model, while holding all other variables fixed. This means that we generate a sample for one variable at a time, based on the values of the other variables in the model.
The process starts with some initial values for all the variables in the model. Then, for each iteration of the algorithm, we randomly select one of the variables and update its value based on the values of the other variables in the model. We keep doing this for all the variables until we have generated enough samples.
Exploring Further
- How the length of the document is treated by LDA