Sampling
- Two families of sampling
- nonprobability sampling
- random sampling (probability based sampling)
- Nonprobability sampling
- convenience sampling - selection based on availability
- snowball sampling - Future samples selected based on exisitng samples
- Judgment sampling
- Quota sampling - You select samples based on quotas for certain slices of data without any randomization
- Random sampling
- simple random sampling - All samples in the population equal probability of being selected
- Stratified sampling - to sample 1% of data that has two classes, A and B, you can sample 1% of class A and 1% of class B. Challenging in case of multilabel tasks
- Weighted sampling
- In weighted sampling, each sample is given a weight, which determines the probability of it being selected.
# Choose two items from the list such that 1, 2, 3, 4 each has
# 20% chance of being selected, while 100 and 1000 each have only 10% chance.
import random
random.choices(population=[1, 2, 3, 4, 100, 1000],
weights=[0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1],
k=2)
# This is equivalent to the following
random.choices(population=[1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 100, 1000],
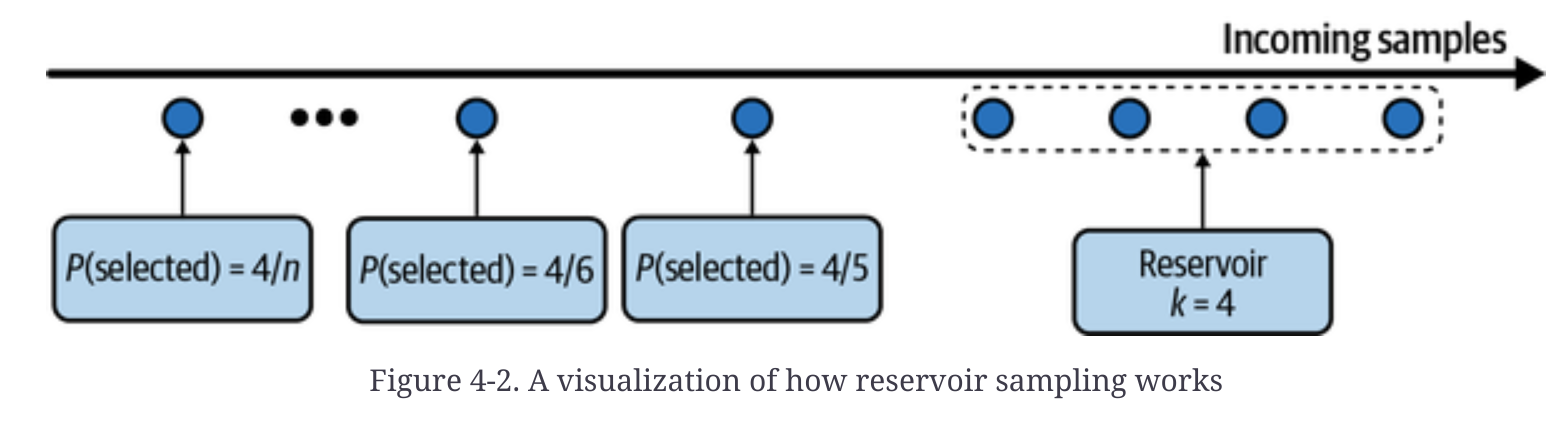
k=2)- Reservoir sampling - useful when have to deal with streaming data

Importance sampling
