Differential Privacy
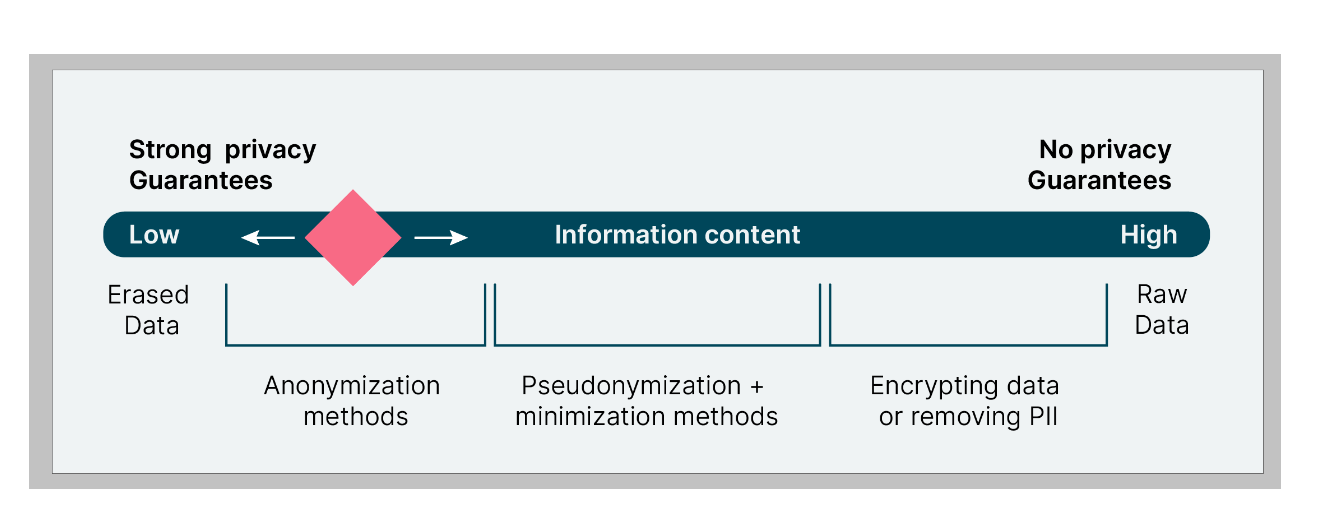
- Anonymize is to remove identifying information from data so that original source cannot be known
- Privacy needs to be understood as a gradient and not a “on” or “off” thing
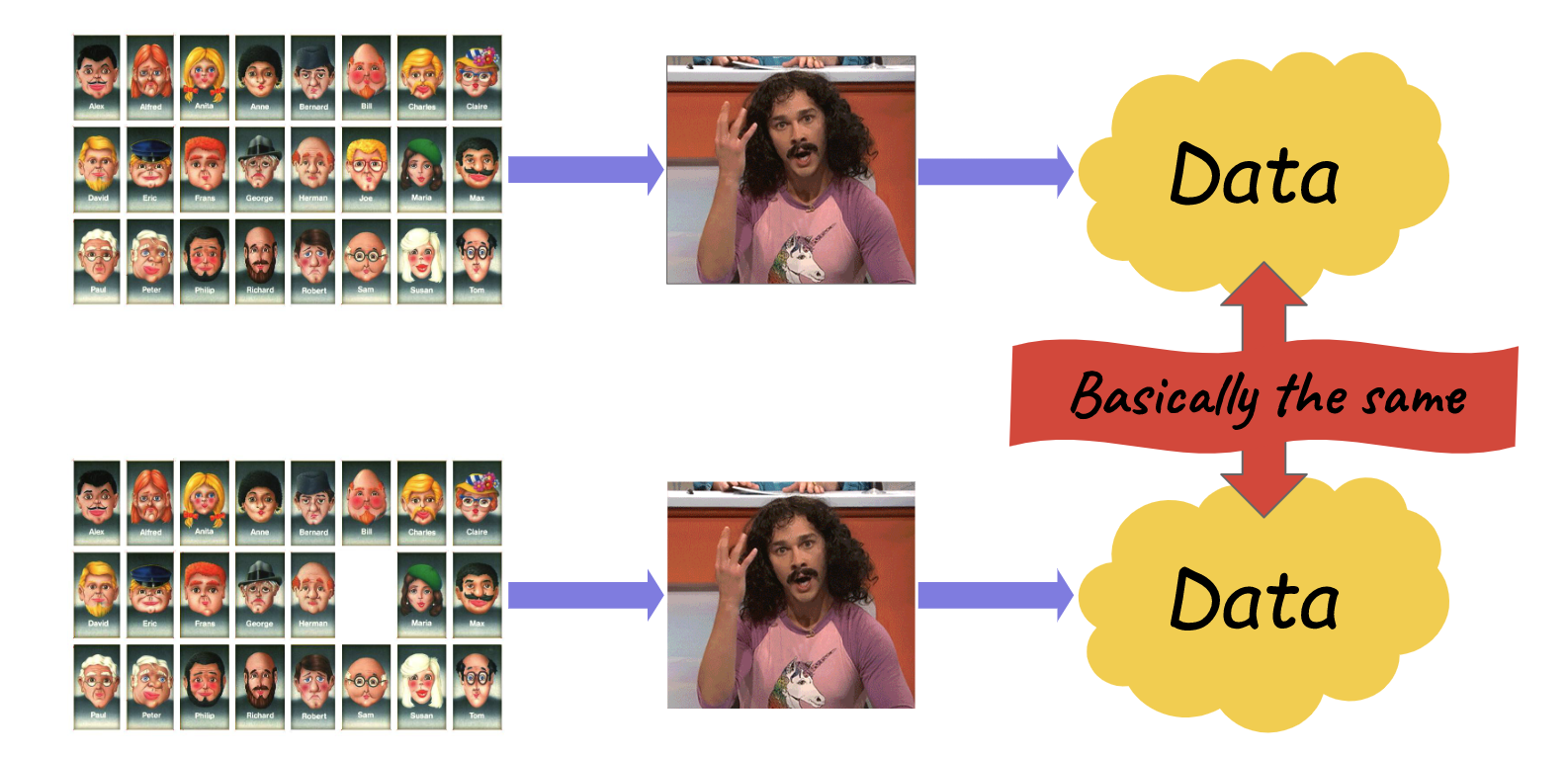
How Differential Privacy works
A process A is epsilon-differentially private if for all databases D1 and D2 which differ in only one individual:
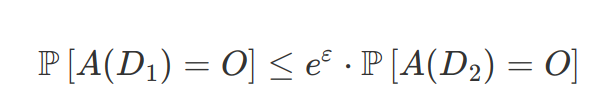
This must be true for all possible outputs O. If epsilon is very close to 0, then exponential of epsilon is very close to 1, so the probabilities are very similar. The bigger epsilon is, the more the probabilities can differ.
- It is a rigorous and scientific definition of privacy-sensitive information release - that defines a limit or bounds on the amount of privacy loss you can have when you release information
- This method focuses on the process rather than the result
- Differential privacy shifts to thinking about what guarantees a particular algorithm can provide by measuring the information that is being continuously released via the algorithm itself.
- Why is differential privacy special:-
- No longer need attack modeling
- We can quantify the privacy loss
- We can compose multiple mechanisms - We can add the epsilon of multiple queries to arrive at the privacy loss for all the queries together.we can allocate budget for the user queries
- Sensitivity measures the maximum change in the query result based on change in the underlying dataset.
Resources for learning Differential Privacy
Courses
Packages and tutorials
python package pydp Tutorials using pydp python package opendp spark package PipelineDP Tensorflow Privacy