Vision Transformers (ViT)
Transformers cannot process grid-structured data. It needs sequences. We need to convert non-sequential signal to a sequence.
Steps in a Vision Transformer
- Split an image into patches
- Flatten the patches
- Produce lower-dimensional linear embeddings from the flattened patches
- Add positional embeddings
- Feed the sequence as an input to standard transformer encoder
- Pretrain the model with image labels
- Finetune on the downstream dataset for image classification
The architecure is the same as the original Attention is all you need paper. The number of blocks is changed.
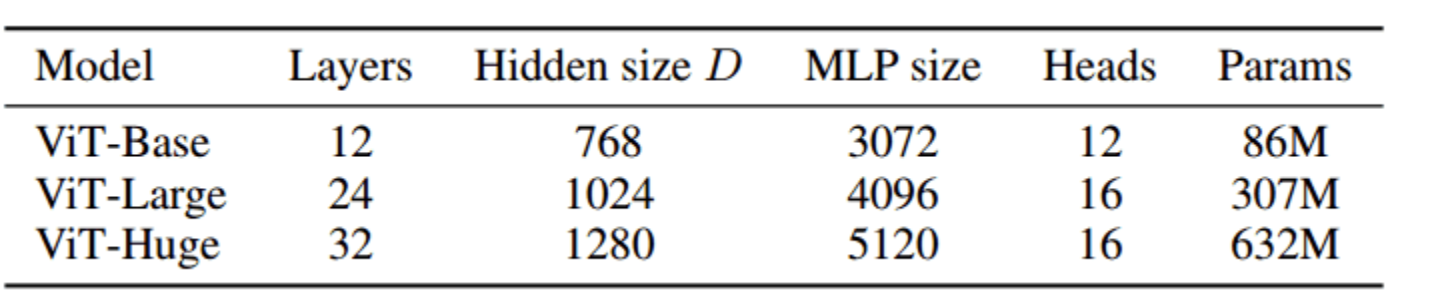
There is no decoder in the architecture.
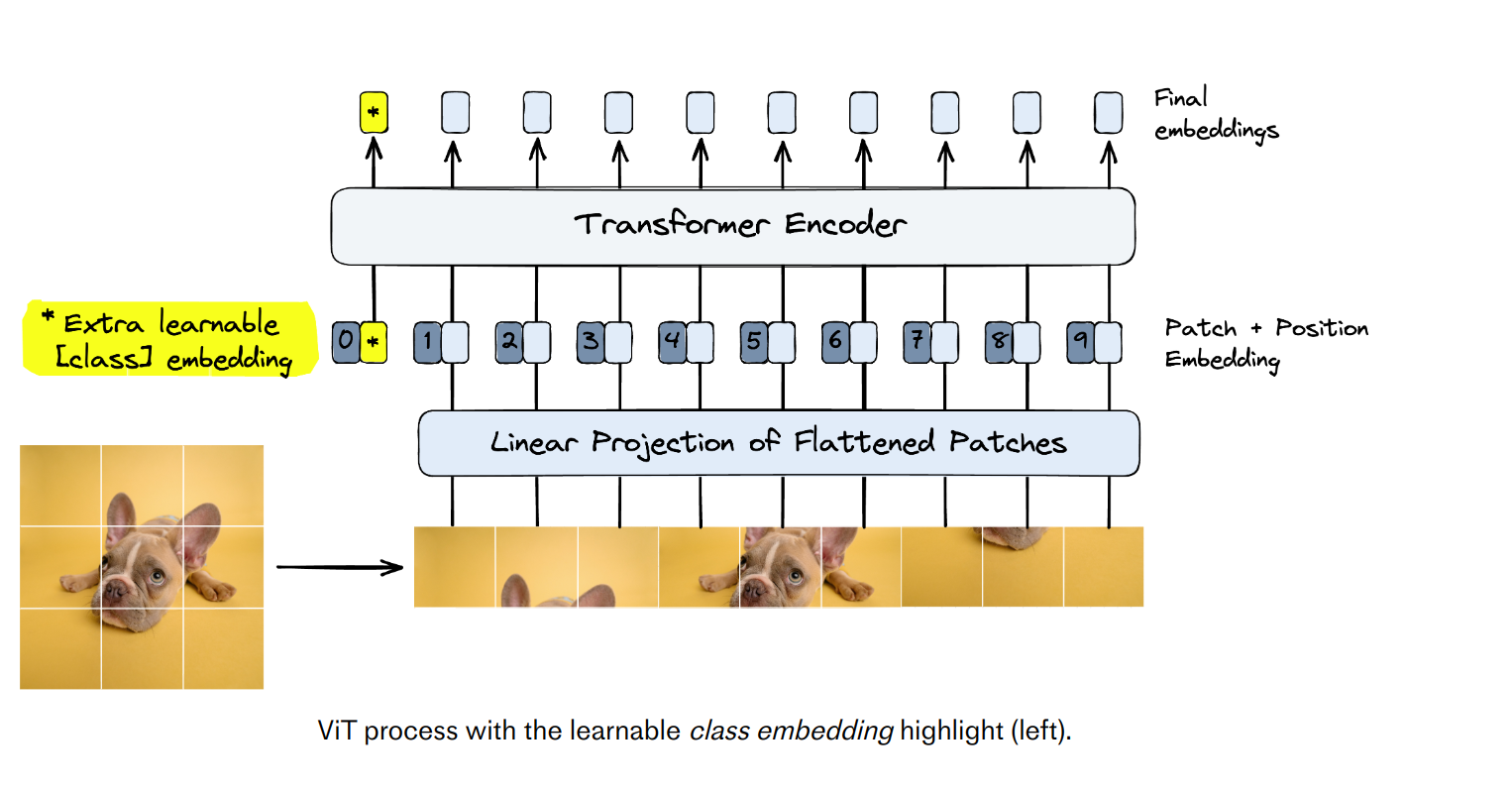
Learnable embedding
[CLS] embedding begins as a “blank slate” for each sentence in BERT. The final output from [CLS] embedding is used as the input into a classification head during pretraining.Using a “blank slate” token as the sole input to a classification head pushes the transformer to learn to encode a “general representation” of the entire sentence into that embedding. ViT applies the same logic by adding a learnable embedding.
Important Details
Specifically, if ViT is trained on datasets with more than 14M (at least :P) images it can approach or beat state-of-the-art CNNs.
ViT is pretrained on the large dataset and then fine-tuned to small ones. The only modification is to discard the prediction head (MLP head) and attach a new D KD×K linear layer, where K is the number of classes of the small dataset.
Even though many positional embedding schemes were applied, no significant difference was found. Hence, after the low-dimensional linear projection, a trainable position embedding is added to the patch representations.
Deep learning is all about scale. Indeed, scale is a key component in pushing the state-of-the-art. In this study7 by Zhai et al. from Google Brain Research, the authors train a slightly modified ViT model with 2 billion parameters, which attains 90.45% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet7. The generalization of this over-parametrized beast is tested on few-shot learning: it reaches 84.86% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet with only 10 examples per class.
Advantages of Vision transformer
- ViTs are robust against data corruptions, image occlusions and adversarial attacks
Drawbacks of Vision transformer
Need More data In CNNs the model knows how to focus, we tell them on how much to focus. In case of transformers, the model does not know how to focus. It pays attention to all the patches and learns where to focus during the training process. Due to this they need huge amounts of data.
Overfitting to small datasets Due to their flexibility they are notorious for overfitting on small datasets. A lot of data augmentation would be required to make it work on small datasets.