Neural GAMs
- EBMs will not work for large datasets and if the data consists of more features
Neural Additive Models:-
- Train a MLP for each feature and sum the outputs across features
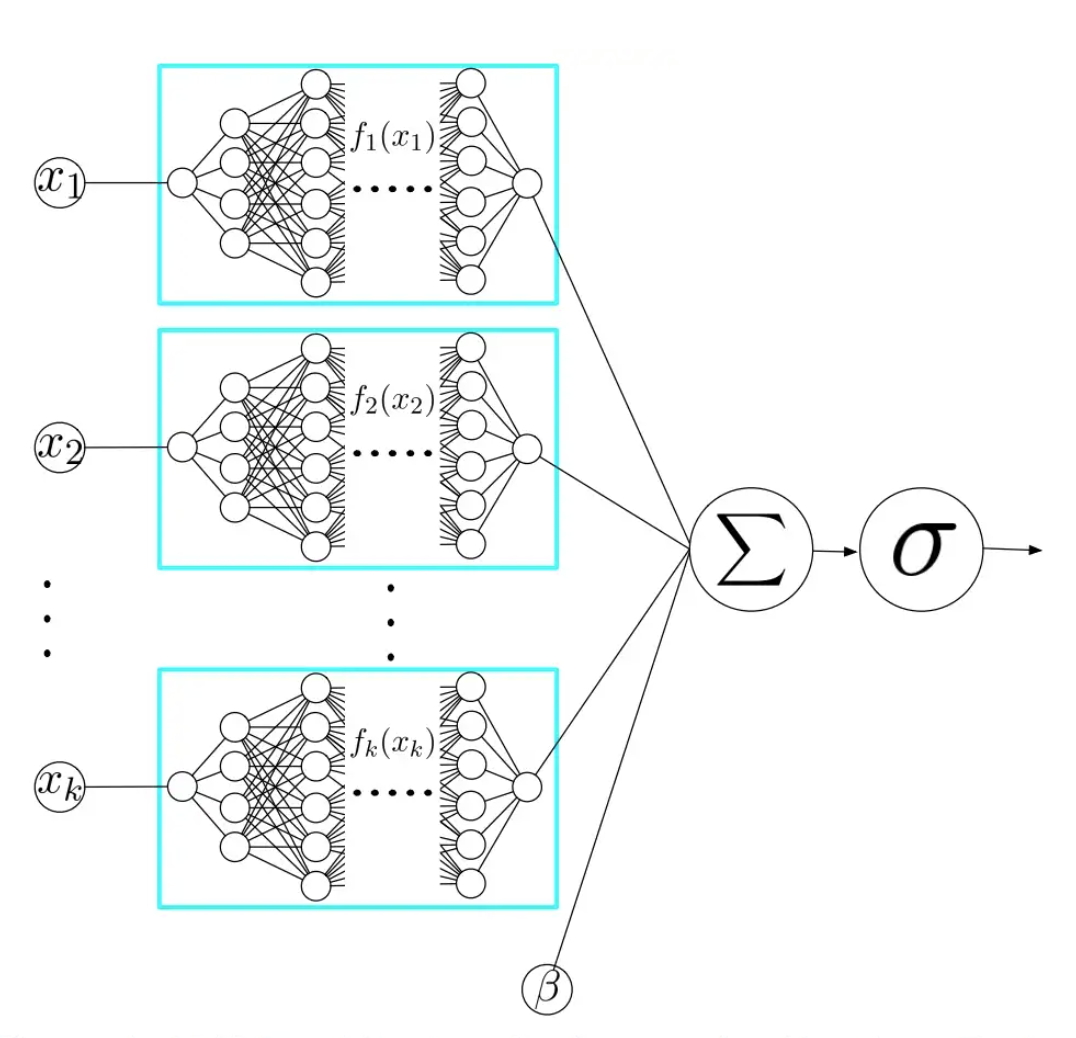
Drawback
- New activation function ExU is required
- As ExU can be overfitting, they need to train multiple neural nets with different random seeds and take average
- Computationally very expensive
NODE-GAM
- Neural Oblivious Decision Trees (NODEs)
- Instead of neurons it uses differentiable oblivious decision trees (ODT) to learn
- In the input layer, instead of summing all the input features and going through a Relu function, NodeGAM uses differentiable attention with temperature annealing to take only 1 feature. This makes sure there is no feature interaction in the model.
- For the connections between layers, NodeGAM uses differentiable gates that only connect trees that belong to the same (set of) features. This also prevents feature interactions.
- Finally, it uses the DenseNet-like skip connections that take all the previous layers’ outputs as inputs. Also, in the output layer, it takes all the intermediate layers embedding as the inputs to the final linear layer as outputs. This helps the gradient to flow through the model since the tree response function is similar to the sigmoid that has a gradient vanishing problem.
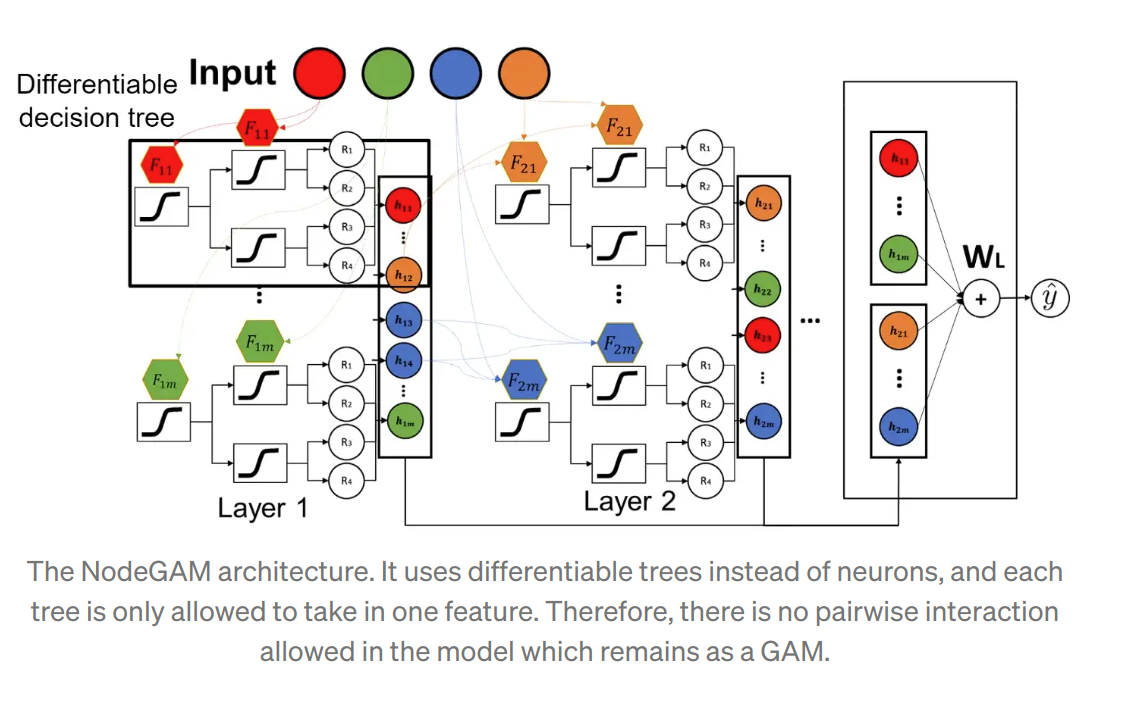
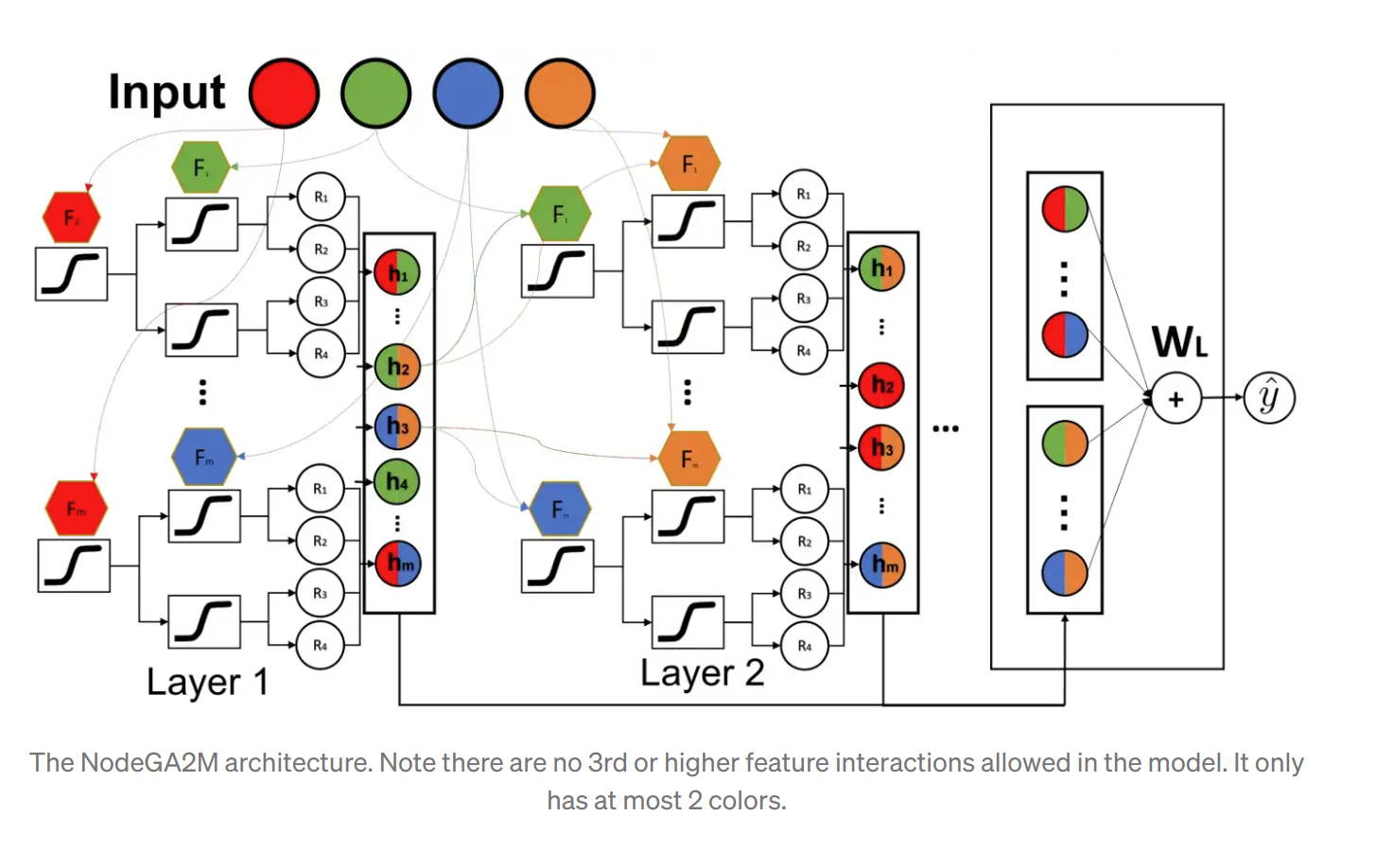
NodeGA2M
- Neural Oblivious Decision Trees (NODEs)
- This method learn pairwise interactions but removes any 3rd or higher-order interactions
- This is achieved by limiting each tree to take at most 2 features. And the connections are only allowed among trees with the same sets of features.
- An attention mechanism is added between layers to improve accuracy
Reference:- Medium Blogpost on NodeGAM code implementation of NodeGAM