Architecture for Image Classification
- A convolution is a NN way to extract and learn a feature through matrix multiplication
- Convolution filters are used to find features such as edges and corners
- These filters are learned through backpropagation
Filtering
- Convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions (f and g) that produces a third function (f * g) expressing how the shape of one is modified by the other.
- A filter (or kernel) is defined and is applied to the image.
- The region the filter is being applied and is called the receptive field.
- An element-wise multiplication is done between the region and filter and adds everything up
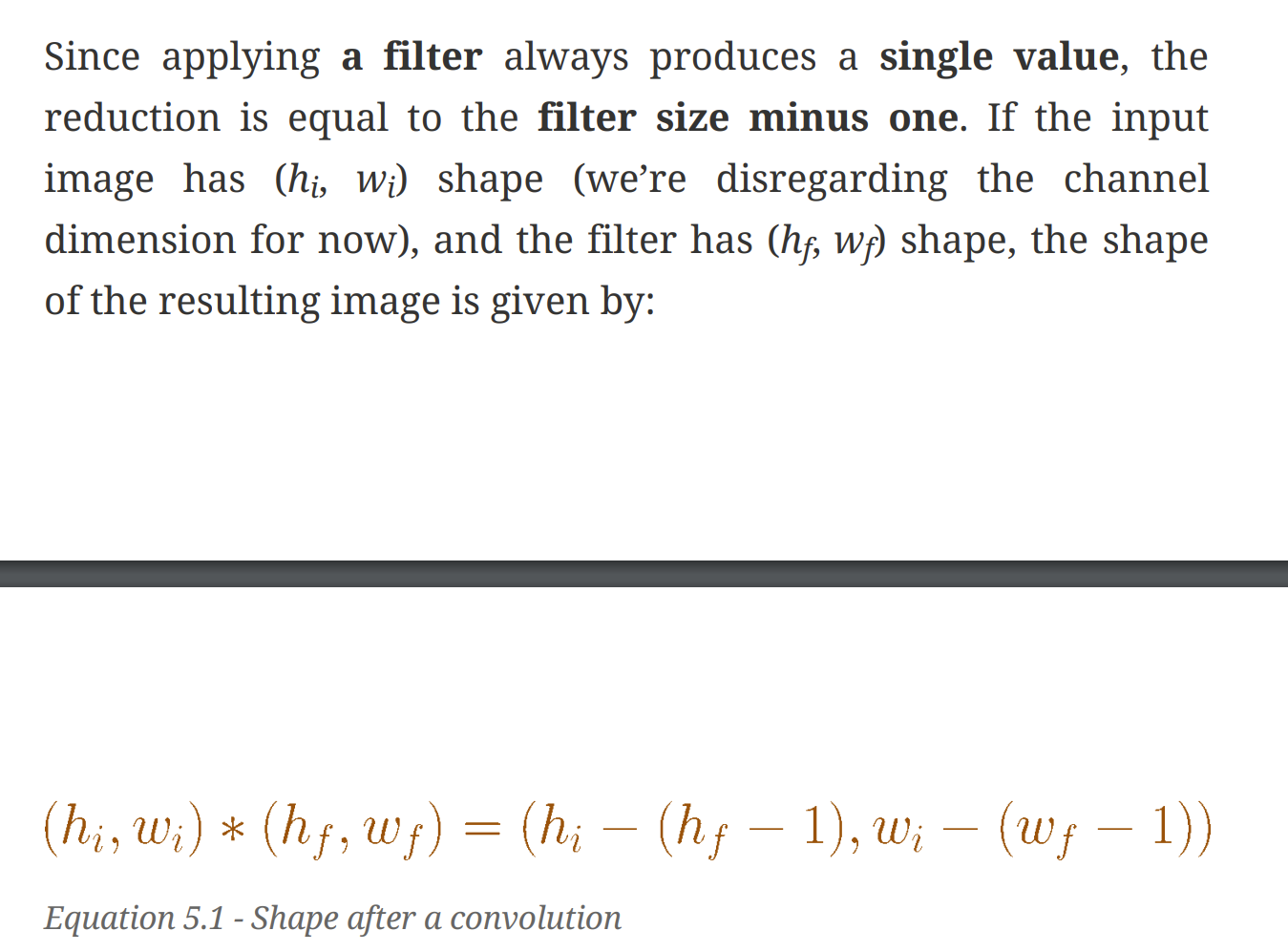
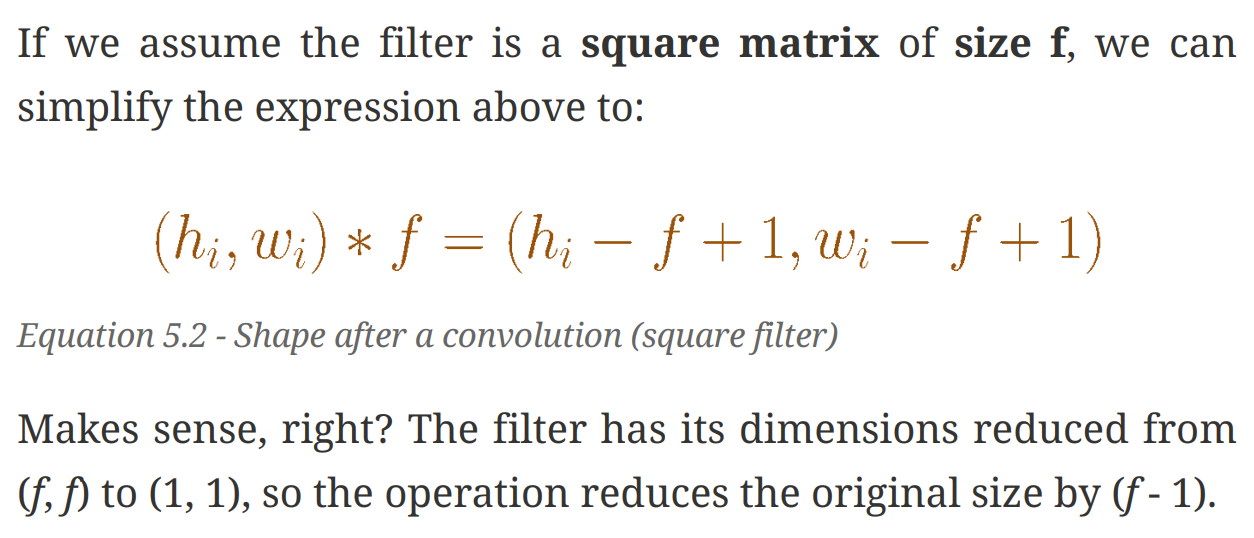
- Doing a convolution produces an image with a reduced size. The bigger the filter, the smaller the resulting image.
- Every filter will have as many channels as the image it is convolving. convolving a three-channel filter over a three-channel image still produces a single value.
- We can have more than one filter.
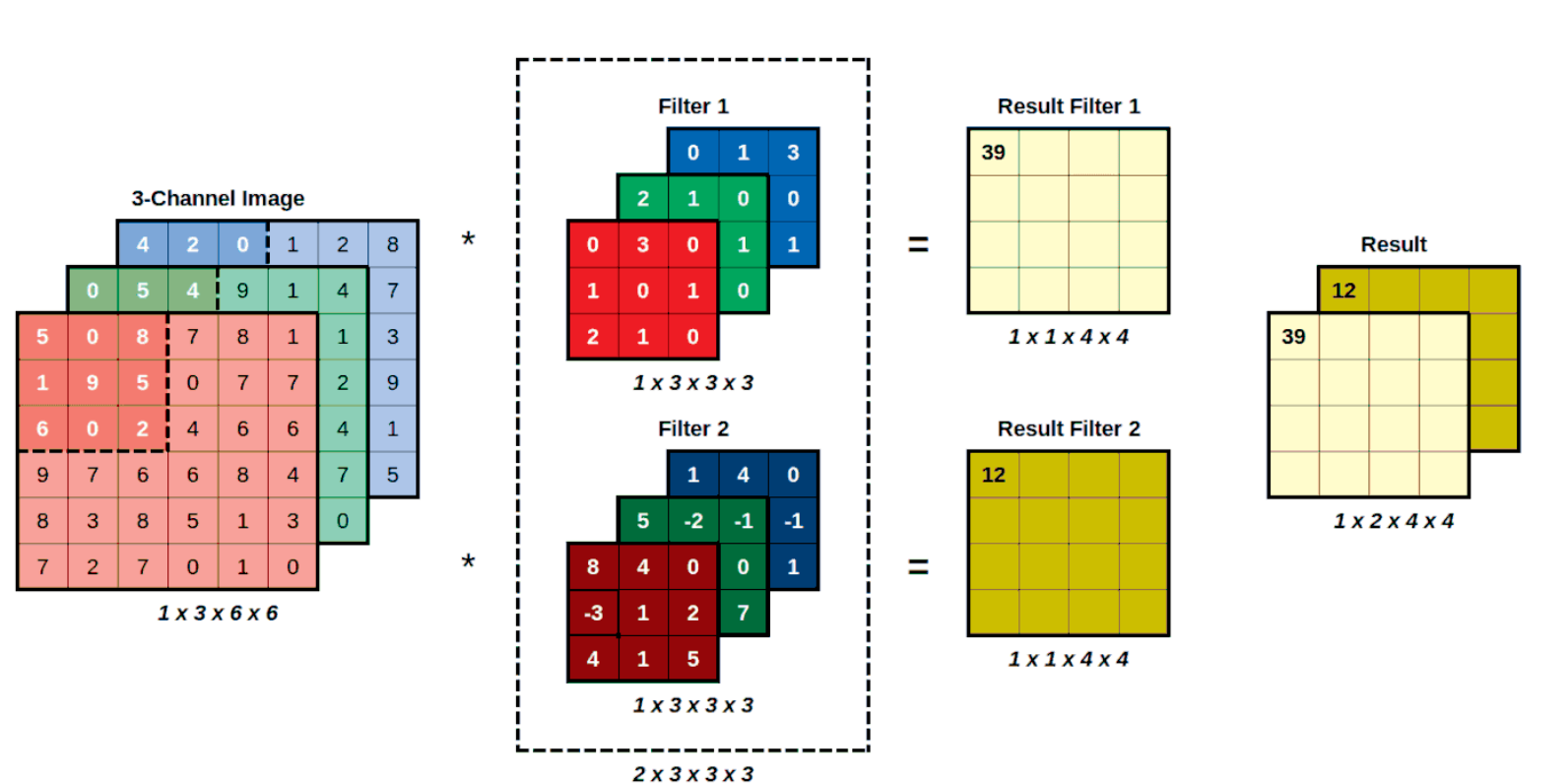
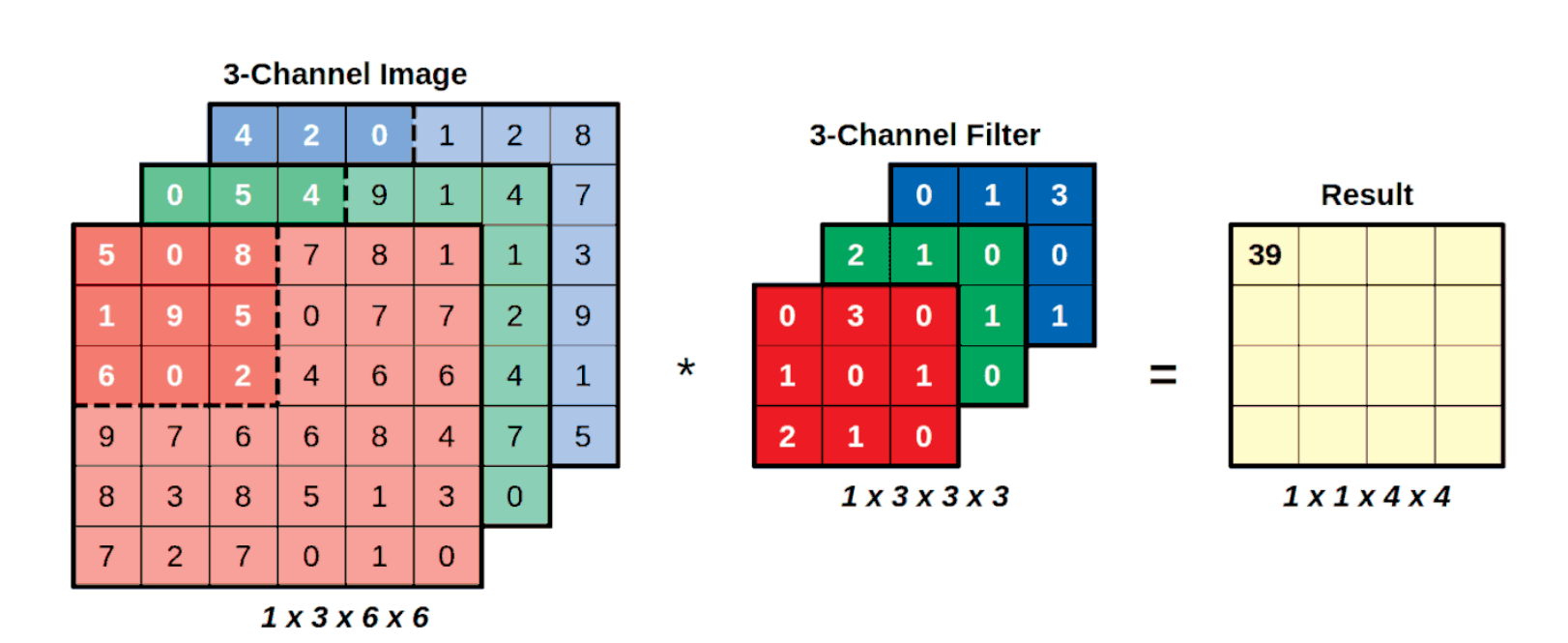
The actual filter, that is, the square matrix used to perform element-wise multiplication is learned using backpropogation
Even if we have only one channel as input, we can have many channels as output. we can also force a convolutional module to use a particular filter by setting its weights
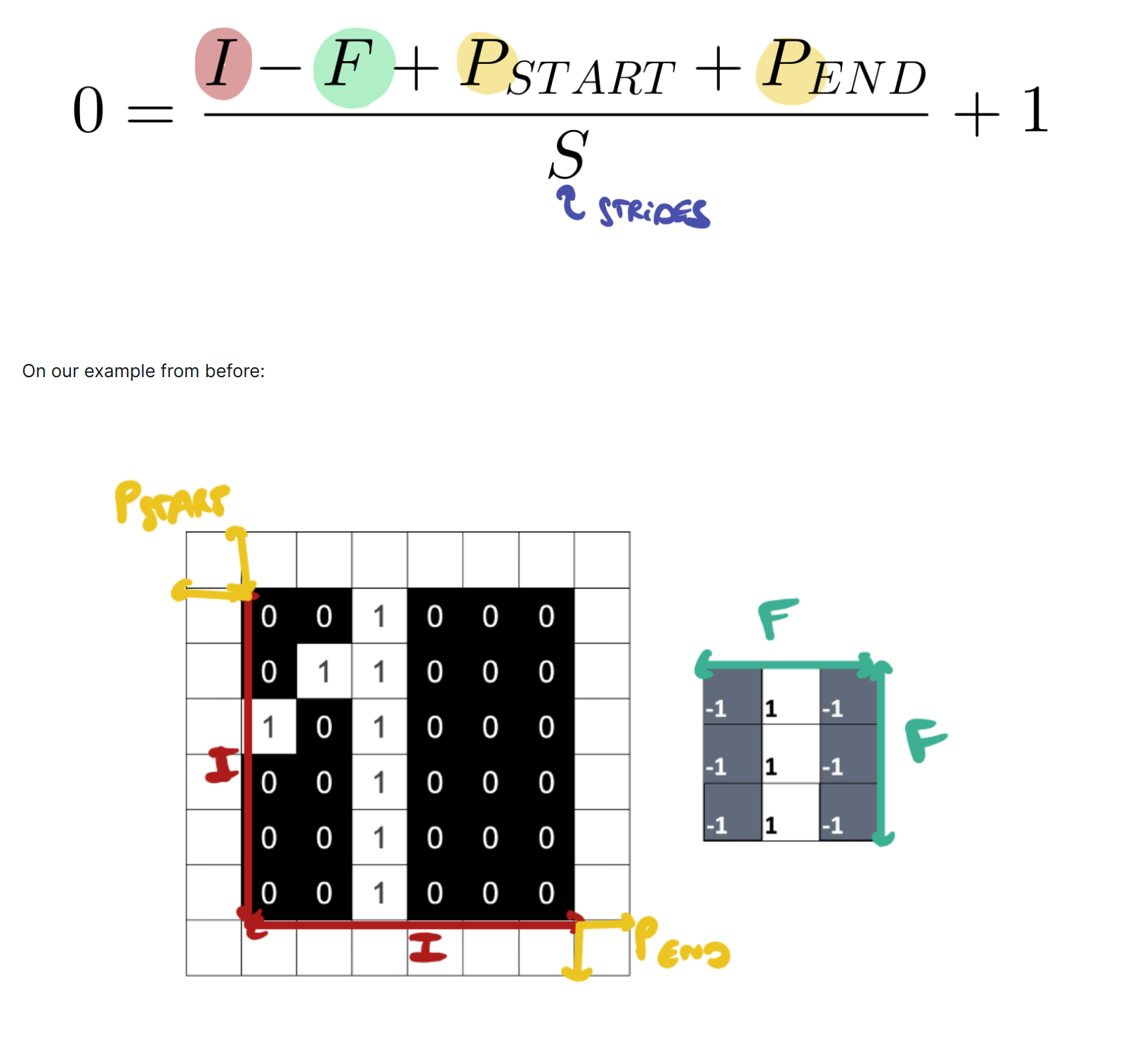
The size of the movement, in pixels, is called a stride. When doing the stride, the filter should not move out of the image (big no-no). The bigger the stride, the smaller the resulting image
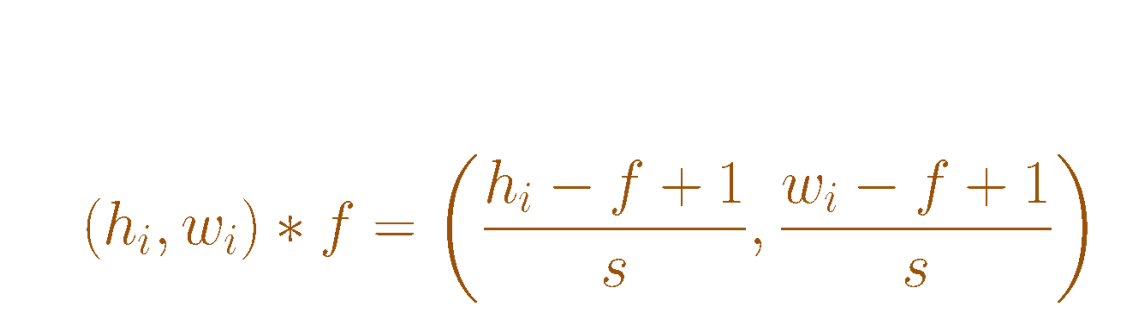
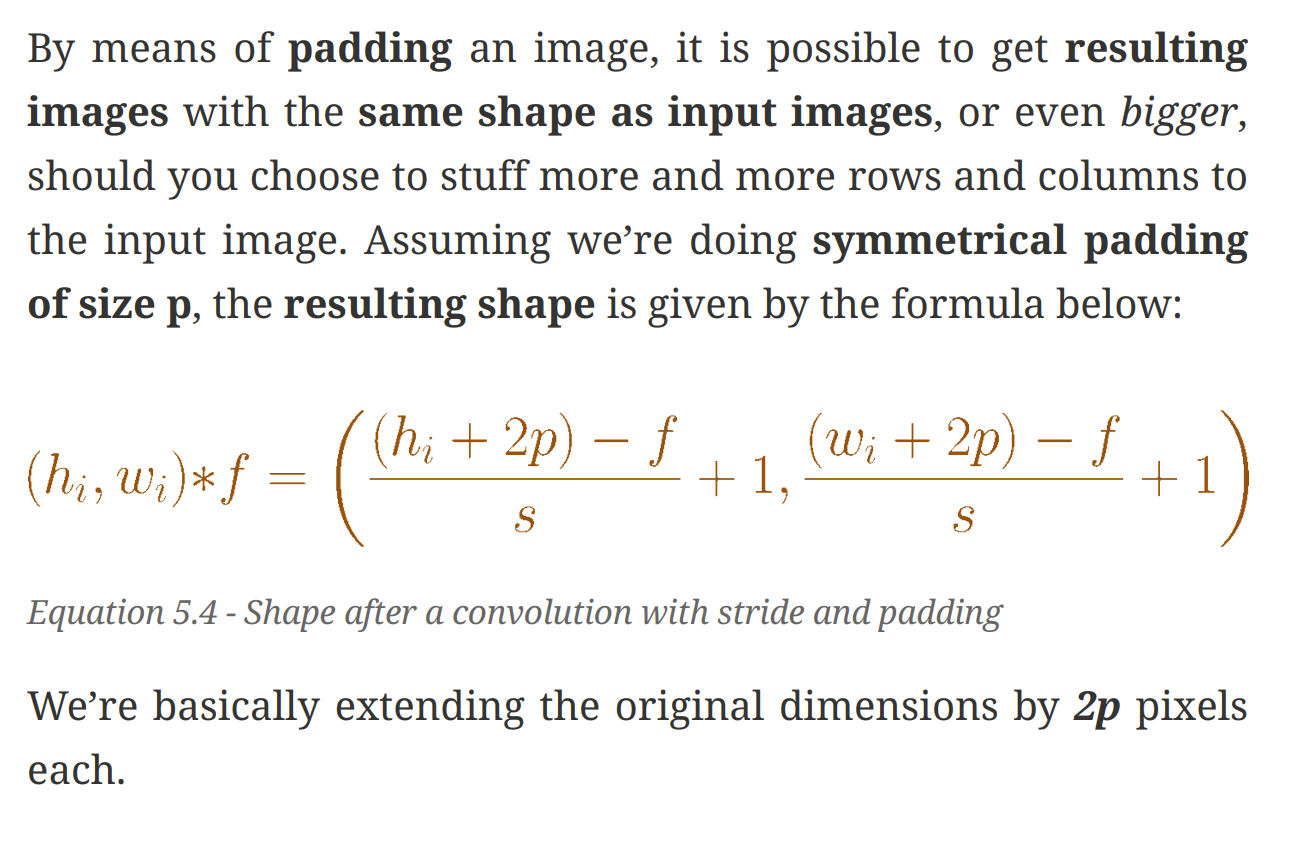
we can use padding if we would like to keep the original image size. we can also add asymmetric padding.
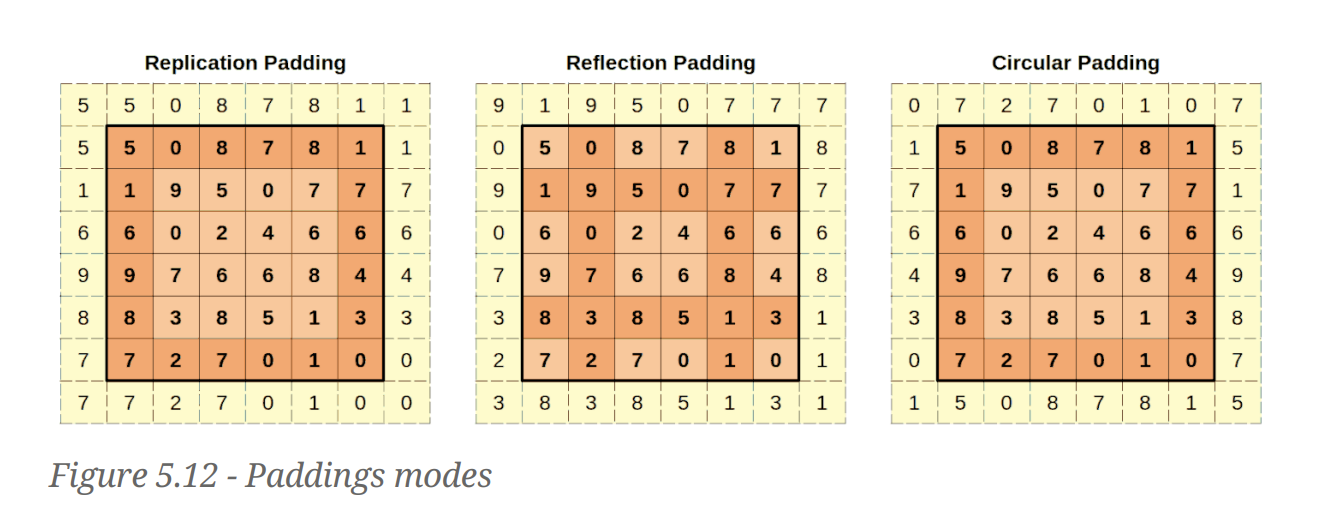
Different Padding modes
Pooling
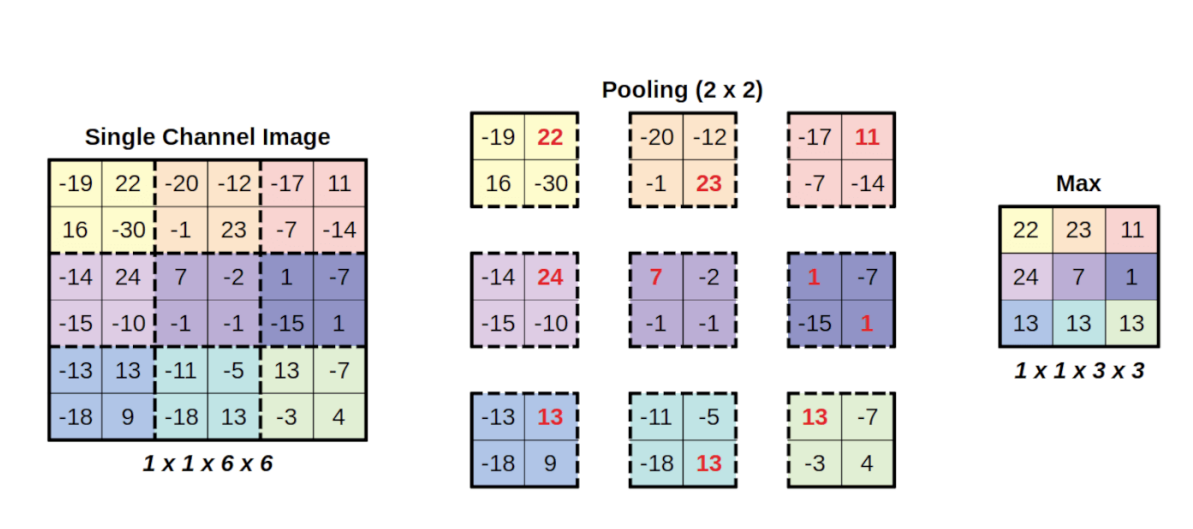
Max pooling The bigger the pooling kernel, the smaller the resulting image
A pooling kernel of two-by-two results in an image whose dimensions are half of the original. A pooling kernel of threeby-three makes the resulting image one third the size of the original, and so on.
The pooling kernel should not go out of the image
Common pooling operations - Max pooling, Average pooling,
Normally the stride will be equal to the dimensions of the square filter. We can also consider other strides as well. In this case there will be overalaps and the pooling works like strides in the convolution layer
It is a technique to downsample the output while keeping the most relevant information
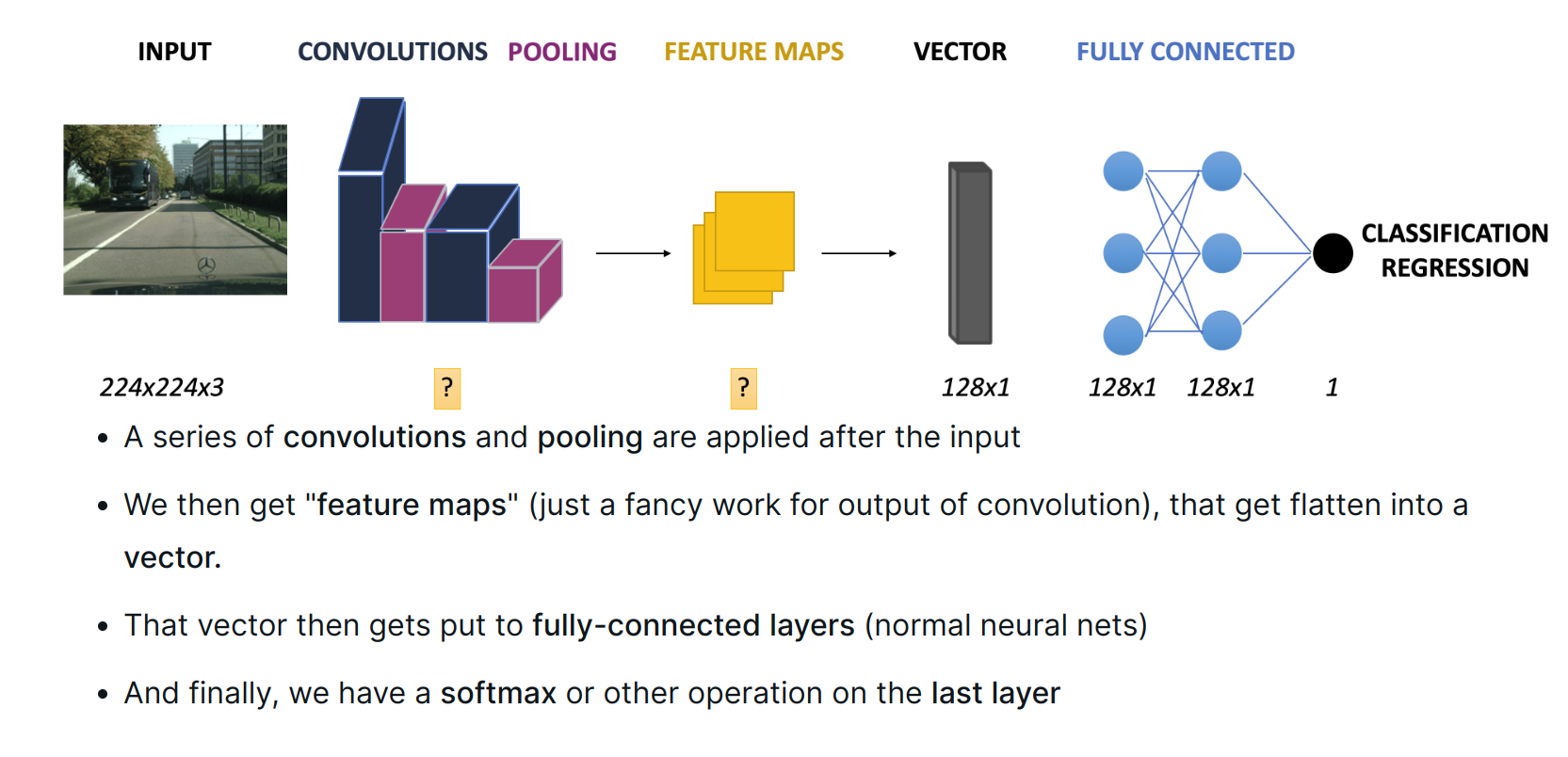
Typical Architecture
- convolution
- Activation function
- pooling
- The number of channels/filters produced by each block is increased as more blocks are added
- Image gets flattened
Batch Norm
- Batch normalization is the process of normalizing each layer’s inputs by using the mean and variance of the values in the current mini-batch - Benefits in faster convergence with higher learning rates