OneFormer: One Transformer to rule Universal Image Segmentation
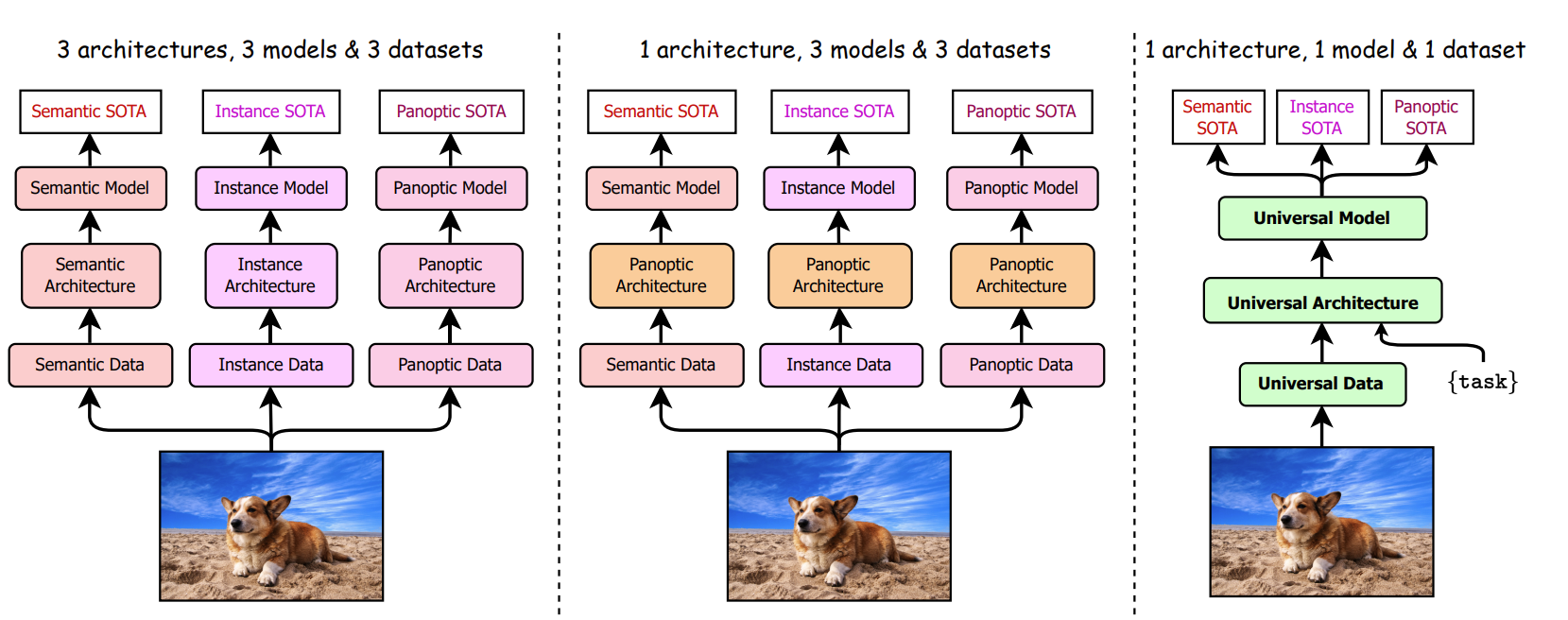
A multi-task universal image segmentation framework which outperforms existing state-of-the-art on all three segmentation tasks by only training once on a panoptic dataset.
A task token is introduced in the form of text, to condition the model on the task {panoptic, instance, semantic} in focus, making the architecture task-guided for training and task-dynamic for inference, all with a single model.
Tasks are uniformly sampled {panoptic, instance, semantic} to ensure the model is unbiased in terms of tasks. Motivated by the ability of panoptic data to capture both semantic and instance information,the semantic and instance labels are derived from the corresponding panoptic annotations during training.
Architecture
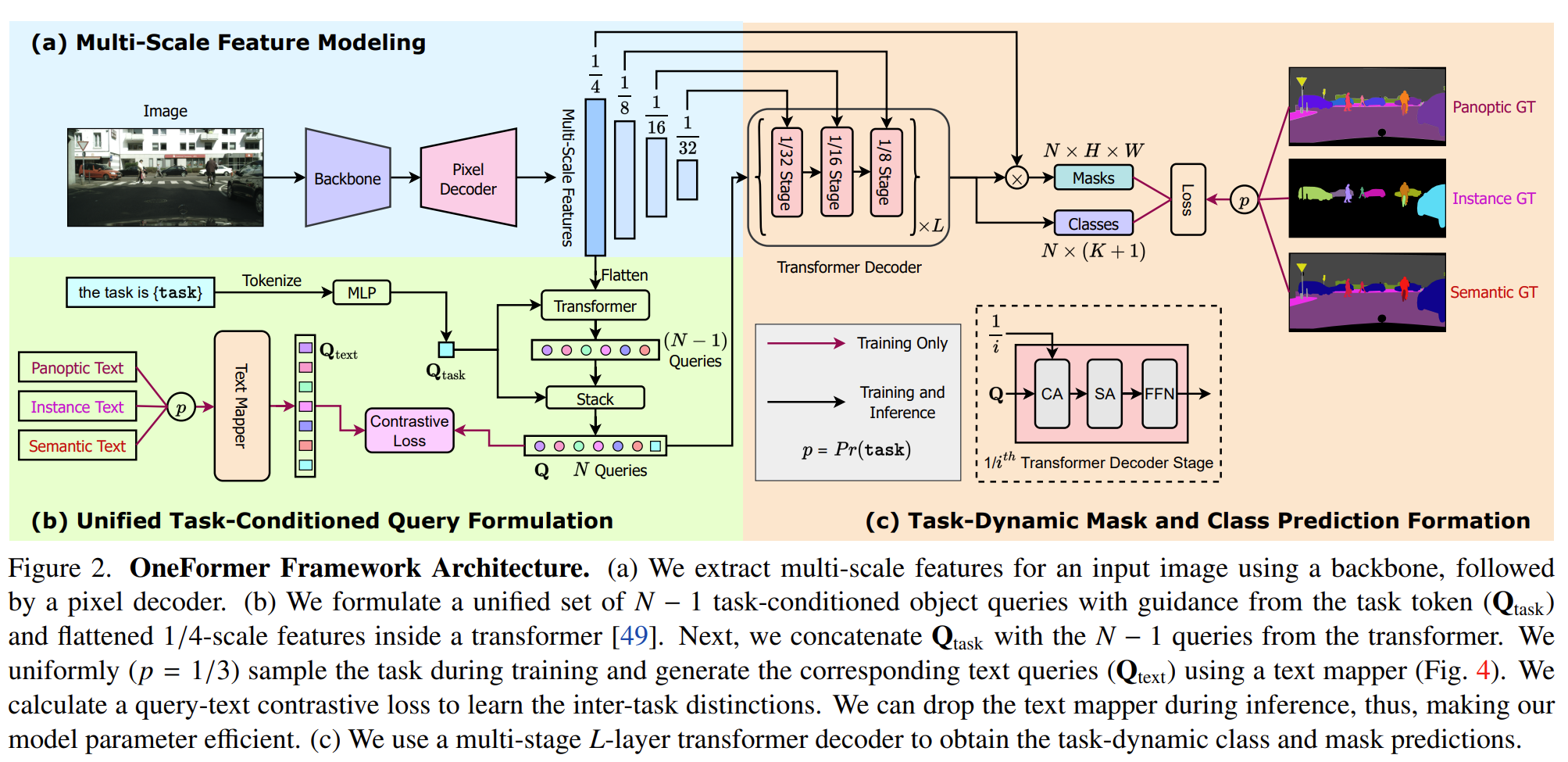
- Uniformely sample the task [panoptic, instance, semantic]
- Task conditioned architecture
- Task specific labels are derived from the corresponding panoptic annotations
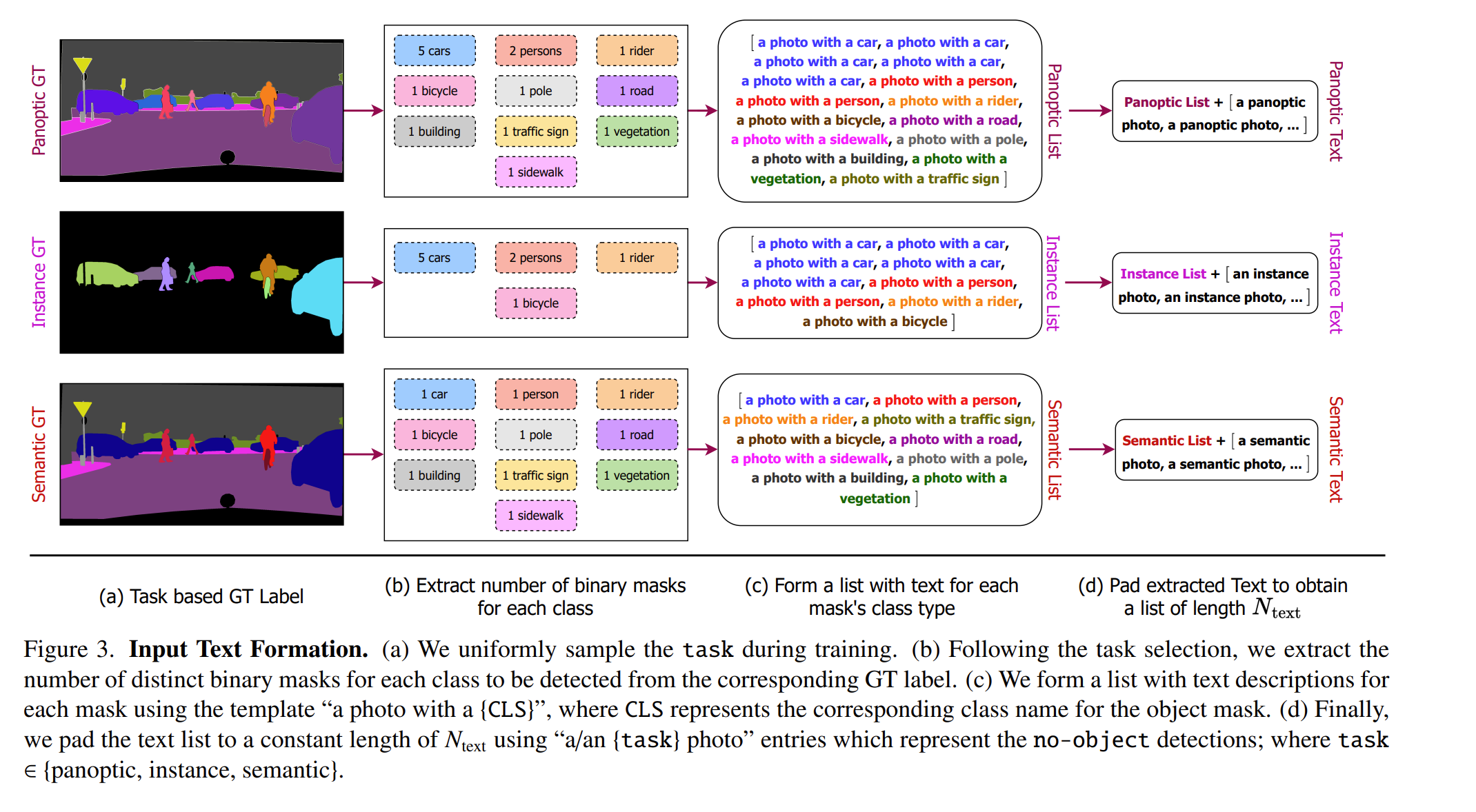
- A set of binary masks are extracted for each category present in the image i.e. task-specific GT label. These set of masks are converted to a list of text. Padding is added to get a constant length, with padded entries representing no-object masks. This padded list is used for computing a query-text contrastive loss
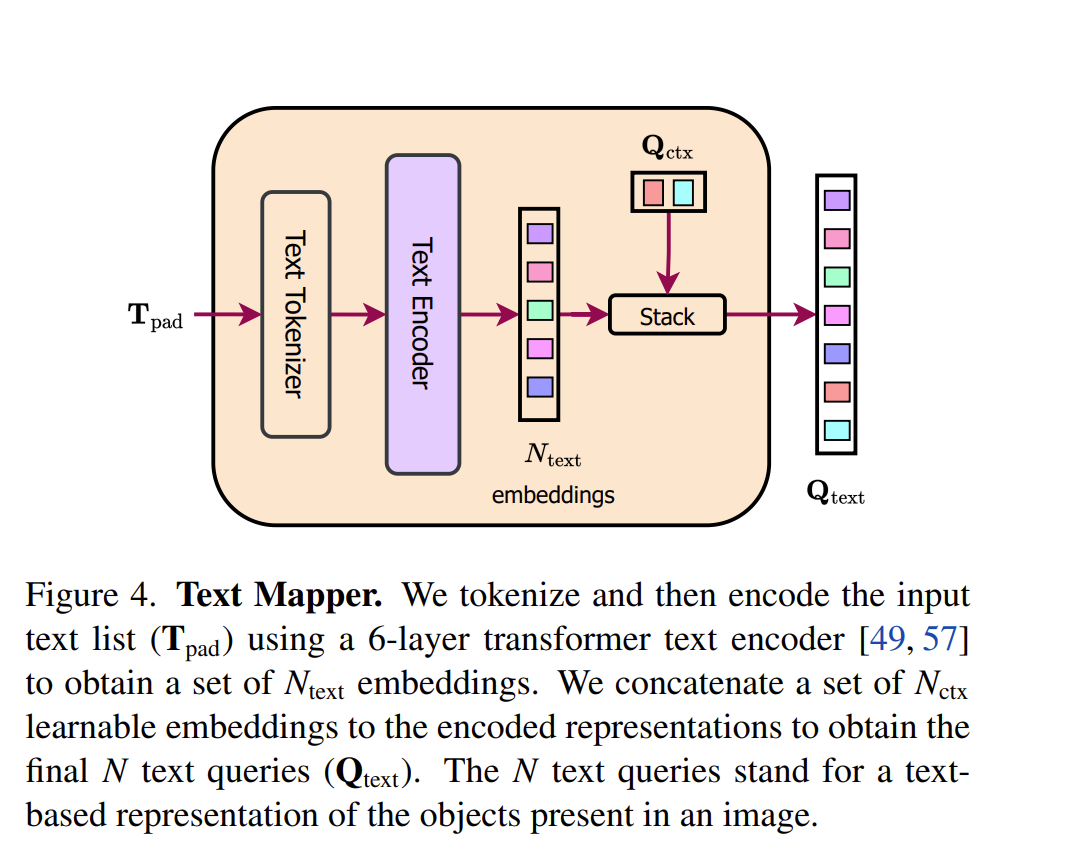
The architecture is conditioned on the task using a task input with the template “the task is {task}”, which is tokenized and mapped to a task token. This task token is used to condition OneFormer on the task.
A contrastive loss is calculated between the task-conditioned image representation and the ground truth derived text and object binary mask.
Backbone and pixel decoder ImageNet pre-trained backbone is used to extract multi-scale feature representations from the input image. Pixel decoder aids the feature modeling by gradually upsampling the backbone features.
Losses Four losses are used with different weights for optimization * Contrastive loss on the queries * Classification cross entropy loss for the class predictions. * A combination of cross-entropy and dice loss are calculated for the mask predictions. Bipartite matching is used between set predictions and ground truths to find least cost assignment.
Results
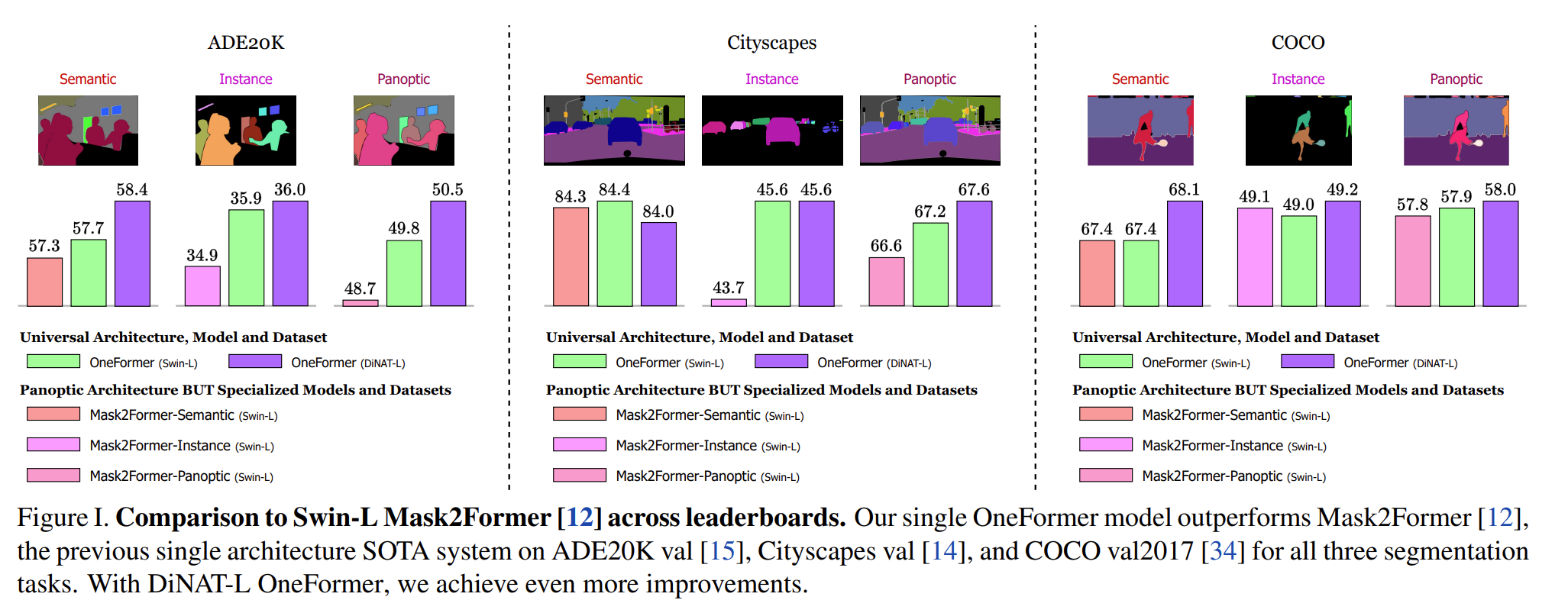
- Evaluated on Cityscapes, ADE20K and COCO datasets
- Panoptic quality (PQ), Average Precision (AP) and mIoU (mean Intersection over union) is used for panoptic, instance and semantic segmentation
OneFormer sets a new state-of-the-art performance on all three segmentation tasks compared with methods using the standard Swin-L backbone, and improves even more with new ConvNeXt and DiNAT backbones.